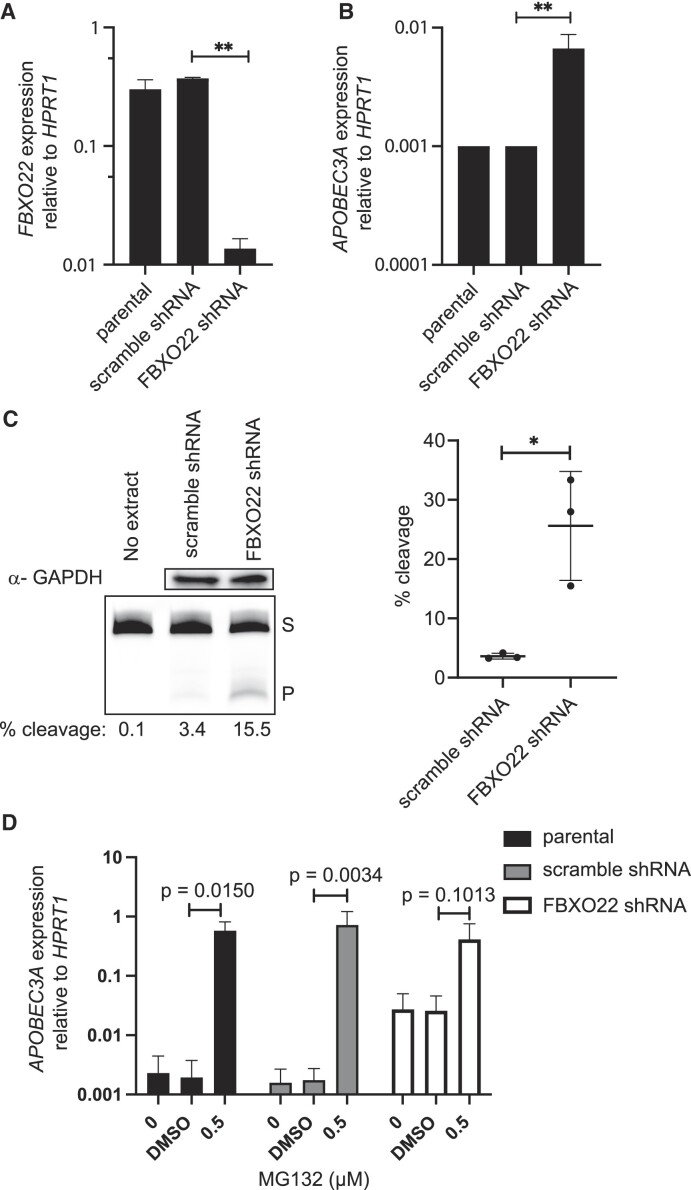
Figure 5.
A3A increase is FBXO22 dependent. FBXO22 shRNA knockdown in MDA-MB-453 cells. (A) FBXO22 expression was reduced 30-fold (ratio paired t-test; P-value 0.0011) leading to (B) a 6.7-fold increase in A3A (ratio paired t-test; P-value 0.0086). (C) Representative images of GAPDH analysis by western blot and denaturing gel of A3A activity assays with MDA-MB-453 cells expressing a scramble shRNA or FBXO22 shRNA knockdown. Percent cleavage of hairpin substrate in activity assays plotted produced significant change from scramble to FBXO22 knockdown (n = 3). Mean shown for the replicates and error bars represent one standard deviation. (D) A3A expression relative to HPRT1 was assessed in the parental, scramble shRNA and FBXO22 shRNA cell lines upon 24 h treatment with 0.5 μM MG132 (n = 3 independent measurements). The parental and scramble shRNA lines had a 296-fold increase (ratio paired t-test; P-value 0.0150) and 416-fold increase (ratio paired t-test; P-value 0.0034), respectively. FBXO22 shRNA did not have a significant increase in A3A (ratio paired t-test; P-value 0.1013). S, substrate; P, product. *P ≤ 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01; ns, non-significant with P-value >0.05.