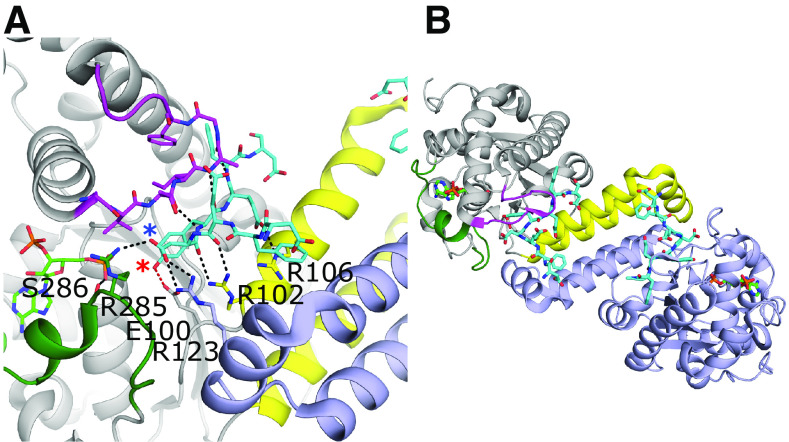
Fig. 5.
Substrate binding and dimerization of TPST-1. (A) Substrate binding site of TPST-1 (PDB code 5WRI) (Tanaka et al., 2017). Residues Arg102 and Arg106 from the α-helix bundle and loop 2 (magenta) contribute significantly to substrate binding. Residues from loop 3 (green) form interactions with both the acceptor (Arg285) and donor substrates (Ser286). Arg123 from the other protomer forms a nonessential interaction with the substrate. The acceptor tyrosine is positioned for catalysis and forms a hydrogen bond with the proposed catalytic base Glu100 (red dashed line). The acceptor hydroxyl on the tyrosine and the Asp at the -1 position of the substrate are designated with red and blue asterisks, respectively. (B) Dimer interface of TPST-1. One protomer is colored light purple, whereas the other is colored gray with the equivalent to loops 1, 2, and 3 of the SULTs colored in yellow, magenta, and dark green, respectively.