Figure 5.
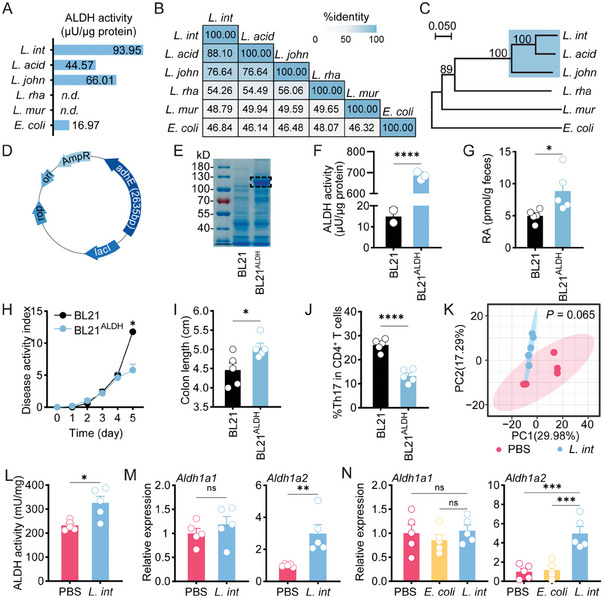
L. intestinalis promoted RA synthesis through its own ALDH and by enhancing host ALDH. A) The ALDH activity was detected in six different species. B) Percentage identity analysis was performed on ALDH protein sequences of six different species. C) Phylogenetic tree analysis of ALDH protein sequences of six different species was constructed. Bootstrap analysis values for 1000 replicates were shown. D–F), Plasmid containg L. intestinalis adhE (D) was transduced into bacterial expression systems BL21ALDH. The ALDH expression and activity were detected (E–F). G–J), Quantification of RA was performed in the feces of acute DSS‐treated mice with BL21 or BL21ALDH gavage (G). The pathology of acute colitis was evaluated between DSS‐treated mice with BL21 or BL21ALDH gavage, by disease activity index (H) and colon length (I), and frequencies of Th17 cells (J) (n = 5). K) β‐diversity of the fecal was compared between chronic DSS‐treated mice with PBS gavage and with L. intestinalis (L. int) gavage (n = 5). L,M) The ALDH activity (L) and related gene expression (M) were detected between colon tissues of DSS‐induced acute colitis mice with PBS, and L. intestinalis (L. int) gavage (n = 5). N) Expression levels of Aldh1a1 and Aldh1a2 were evaluated in bulk colon samples from chronic DSS‐treated mice with gavage of PBS, E. coli, and L. intestinalis (L. int) (n = 5). Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. ns, no significance; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. p values were based on Student's t‐test, PERMANOVA test, and one‐way ANOVA with post‐hoc test.
