Figure 7.
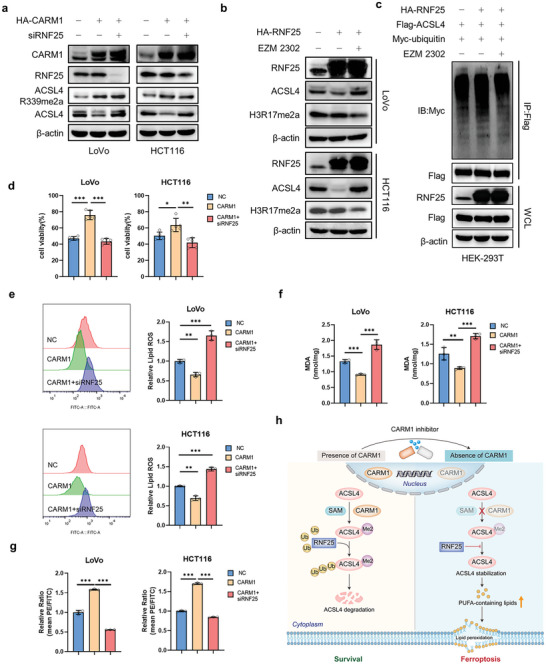
RNF25 knockdown inhibits CARM1‐induced ferroptosis resistance. a) Western blot analysis of LoVo and HCT116 cells transfected with the indicated plasmid and siRNAs. Protein levels of CARM1, RNF25, ACSL4 and ACSL4 R339me2a were assayed. b) Western blot analysis of vector‐ and RNF25‐overexpressing LoVo and HCT116 cells treated with DMSO or 10 × 10−9 m EZM2302 for 24 h. Protein levels of RNF25, ACSL4, and H3R17me2a were assayed. c) HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with or without 10 × 10−9 m EZM2302 for 24 h. Immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti‐Flag antibody and Western blotting with an anti‐Myc antibody were performed to detect the ubiquitination level of ACSL4. d) Cell viability was assayed in the indicated LoVo and HCT116 cells as (a) treated with 2. 5 × 10−6 m RSL3 for 12 h (n = 5 independent experiments). e,f) Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and relative lipid ROS were assayed in the indicated LoVo and HCT116 cells treated with 2. 5 × 10−6 m RSL3 for 12 h (n = 3 independent experiments). g) Mitochondrial membrane potential was detected for the same cells as (e) by using fluorescence staining of mitochondria with JC‐1 dye (n = 3 independent experiments). h) Schematic diagram of our hypothesis about this project. The data shown represent the mean ± SD. Comparisons were made by using one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's test; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
