Figure 2.
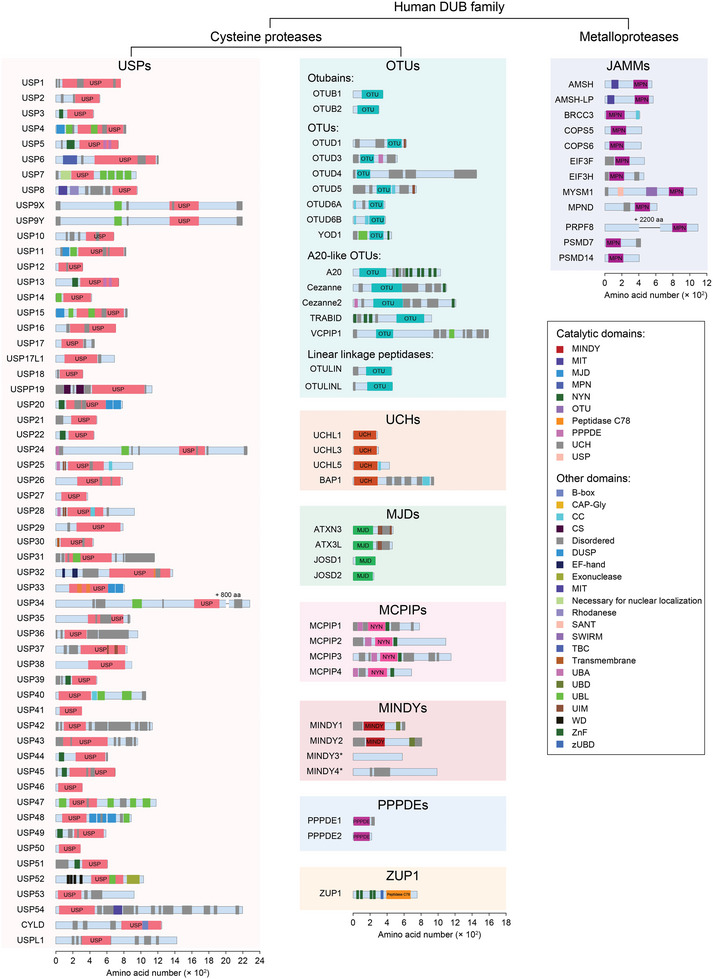
Subfamilies and domain structure of the human DUBs. The human DUBs are classified into six families of cysteine proteases, including ubiquitin‐specific proteases (USPs), ovarian tumor proteases (OTUs), ubiquitin C‐terminal hydrolases (UCHs), Machado–Joseph domain‐containing proteases (MJDs) or Josephins, monocyte chemotactic protein‐inducing proteins (MCPIPs), the motif interacting with ubiquitin (MIU)‐containing novel DUB family (MINDYs), permutated papain fold peptidase of DsRNA viruses and eukaryotes (PPPDEs), zinc finger containing Ubiquitin Peptidase 1 (ZUP1) or zinc finger with UFM1‐specific peptidase domain protein/C6orf113/ZUP1 (ZUFSP); and one metalloprotease subfamily, i.e., JAB1/MPN/MOV34 metalloenzymes (JAMMs, also known as MPN+). CAP‐Gly, cytoskeleton‐associated protein‐glycine‐rich; CC, coiled‐coil; CS, CHORD‐containing proteins and SGT1; MIT, the microtubule interacting and trafficking; MPN, Mpr1/Pad1 N‐terminal; MIT, the microtubule interacting and trafficking; NYN, Nedd4‐BP1, YacP nucleases; SANT, SWI3, ADA2, N‐CoR and TFIIIB DNA‐binding; SWIRM, SWI3P, RSC8P and MOIRA; TBC, Tre2–Bub2–Cdc16; UBA, ubiquitin‐associated; UBD, ubiquitin‐binding domain; UBL, Ubiquitin‐like; UIM, ubiquitin‐interacting motif; ZnF, zinc finger. Numbers with a "+" indicate the number of amino acids is not shown in the sequence. "*" indicates there is no catalytic domain annotated.
