Fig. 3.
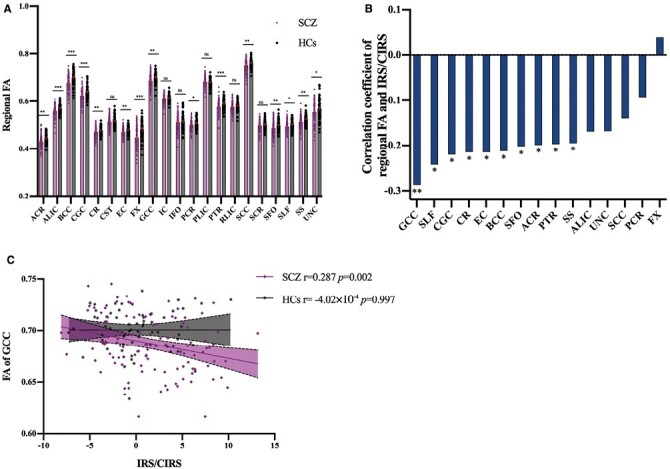
Correlation of regional fractional anisotropy (FA) and inflammatory response system (IRS)/CIRS. FA of 15 white matter microstructural regions were significantly lower in SCZ (A). 10 of them were nominally significantly associated with IRS/CIRS ratio, regarding age, sex, education, body mass index, and total intracranial volume as covariates. (all P < .05) (B). Only FA of GCC and IRS/CIRS was significantly negatively correlated in schizophrenia patients (P= .002, significant after FDR), but not in HCs (P > .05) (C) SCZ, patients with schizophrenia; HCs, healthy controls; ACR, anterior corona radiata; ALIC, anterior limb of internal capsule; BCC, body of corpus callosum; CGC, cingulum; CR, corona radiata; CST, cortico-spinal tract; EC, external capsule; FX, fornix; GCC, genu of corpus callosum; IC, internal capsule; IFO, inferior frontal occipital fasciculus; PCR, posterior corona radiata; PLIC, posterior limb of internal capsule; PTR, posterior thalamic radiation; RLIC, retrolenticular limb of the internal capsule; SCC, splenium of corpus callosum; SCR, superior corona radiata; SFO, superior fronto-occipital fasciculus; SLF, superior longitudinal fasciculus; UNC, uncinate fasciculus; SS, sagittal striatum. * Significant at P < .05; ** Significant at P < .01; *** Significant at P < .001; ns, not significant.
