Fig. 1 |. Oncogenic ALK signaling.
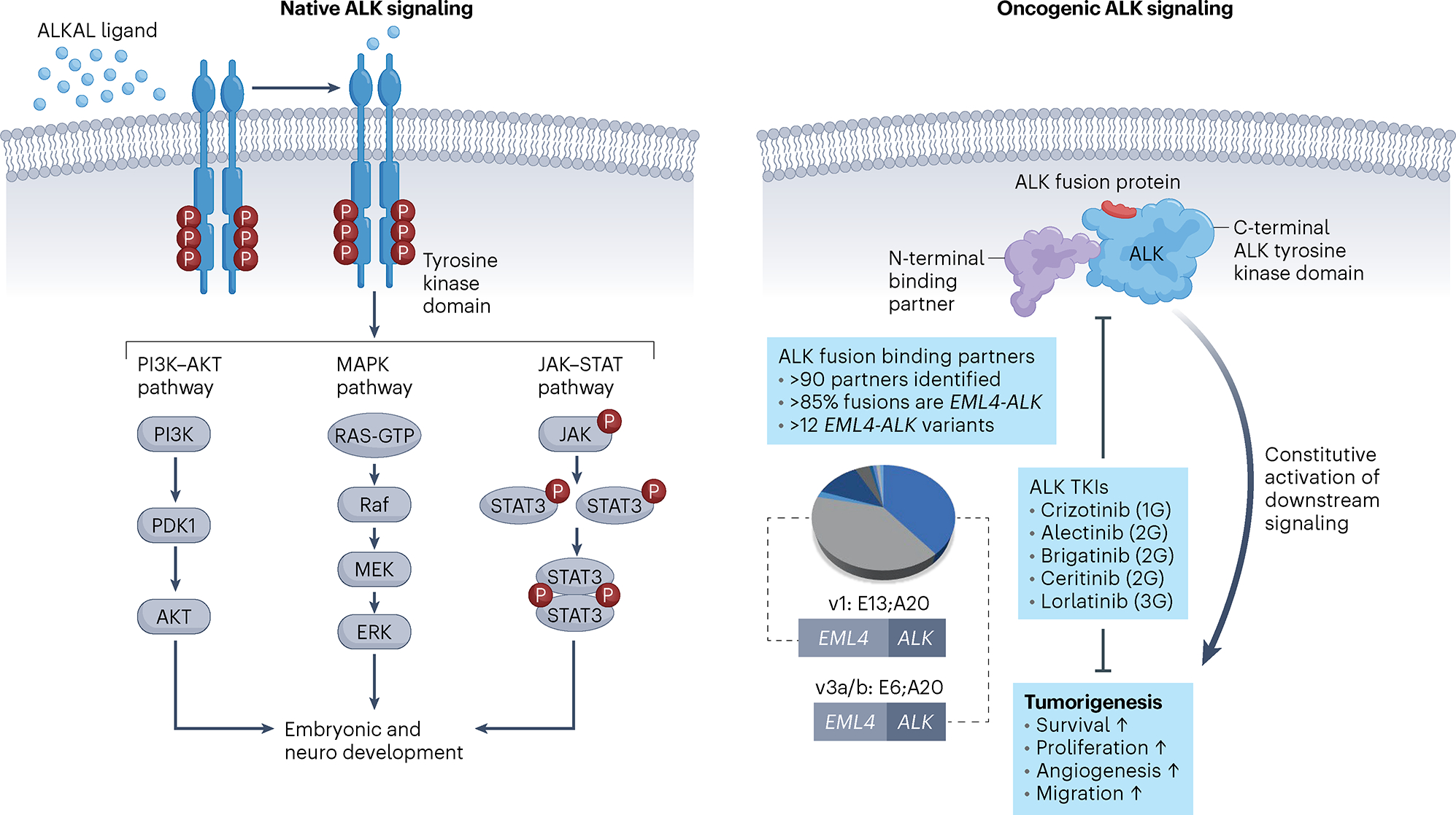
Left, wild-type ALK is a plasma membrane-bound RTK that undergoes autophosphorylation upon ligand binding and receptor oligomerization. ALK activates downstream signaling pathways that contribute to organ development and homeostasis. Right, a chromosomal translocation leads to formation of an ALK fusion gene and translation of an ALK chimeric oncoprotein that is composed of the C-terminal kinase domain of ALK joined with various N-terminal, non-kinase fusion partners. Constitutive activation of ALK promotes cell survival pathways and tumorigenesis. Although many ALK binding partners have been elucidated across all tumor types, the EML4–ALK fusion is the most common, of which EML4-ALK variant 1 (E13;A20) and variant 3 (E6;A20) are the most prevalent in lung cancer. FDA-approved ALK TKIs and their generation are depicted. PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; v, variant; 1G, first generation; 2G, second generation; 3G, third generation.
