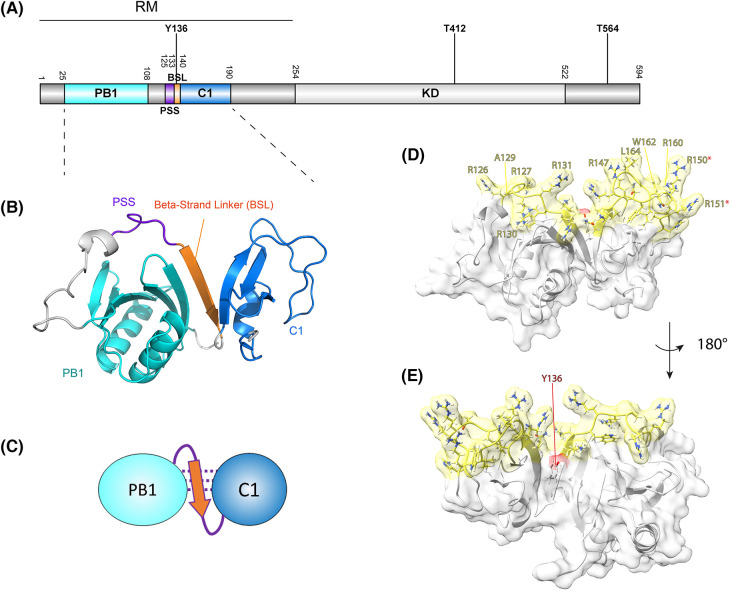
Figure 1. The aPKC N-terminal domains are predicted to be organized into a single functional module, the regulatory module (RM), with membrane binding determinants oriented in a single continuous surface.
(A) Representation of the primary structure of aPKC (human aPKCι residue numbering) with protein domains and the three most abundantly detected phosphorylation sites indicated (cf. PhosphoSitePlus database). RM, regulatory module; PB1, Phox and Bem1 domain; PSS, Pseudo-substrate sequence; BSL, beta-strand linker; KD, kinase domain; T412, activation loop residue; T564, turn motif residue. (B) AlphaFold2 colab prediction of the aPKCRM, with the PB1 domain (cyan), PSS (purple) linked via a Beta-Strand Linker (orange) to the C1 domain (blue). Figure generated in PyMol. (C) Schematic representation of B. (D) Surface representation of the RM with the predicted lipid-binding residues within the RM color coded in yellow. Residues involved in membrane-association as identified in [11] are labeled. Arg150/151 are part of a NLS as identified in [21] and denoted with a red asterisk. Figure generated in ChimeraX. (E) Indication of the Tyr-136 residue location, which in the unphosphorylated state is part of the BSL. Figure panels B–E are adapted from [11].