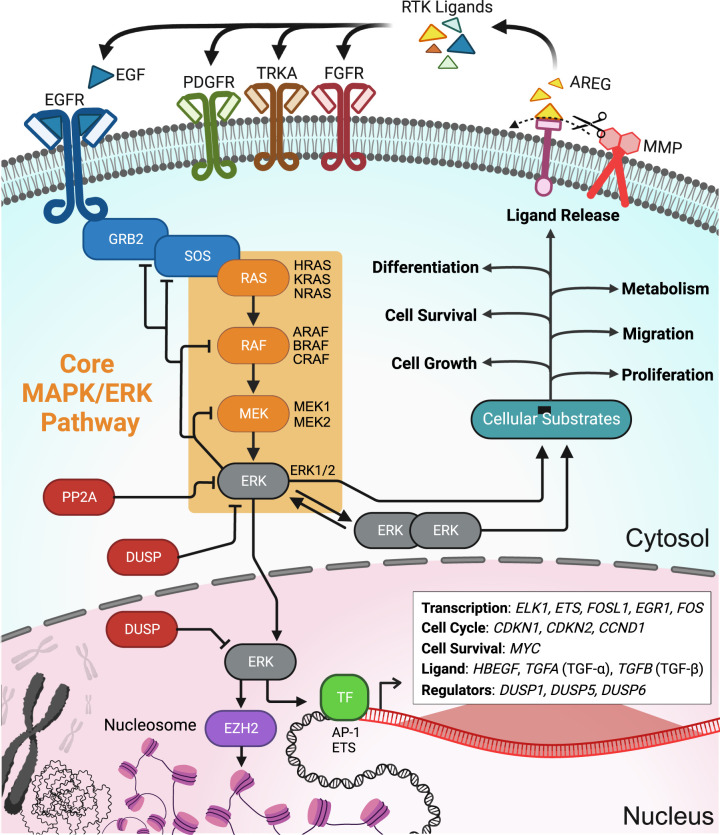
Figure 1. The central ERK signaling pathway.
Initiation of the MAPK/ERK pathway begins with ligand binding of tyrosine receptor kinases (RTKs). This begins the phosphorylation cascade and activation of the core MAPK/ERK pathway consisting of RAS, RAF, MEK, and ERK (orange box, individual isoforms are listed). Active ERK can translocate to the nucleus, where it stimulates gene expression, or dimerize and phosphorylate cytoplasmic substrates. Depending on ERK dynamics, several gene expression programs can be activated, including cell cycle, cell survival, and ligand production (pathways bolded and specific genes listed in the box within the nucleus). Outside the nucleus, ERK regulates cytoplasmic proteins involved in cell growth, metabolism, and differentiation. Pathway termination is regulated by numerous phosphatases (PP2A and DUSPs), as well as several negative feedback loops mediated by ERK phosphorylation. For a comprehensive discussion of additional molecular details see [1]. TF, transcription factors.