Figure 1. Longevity of Anti–MPXV H3L IgG Titers after MVA-BN Vaccination.
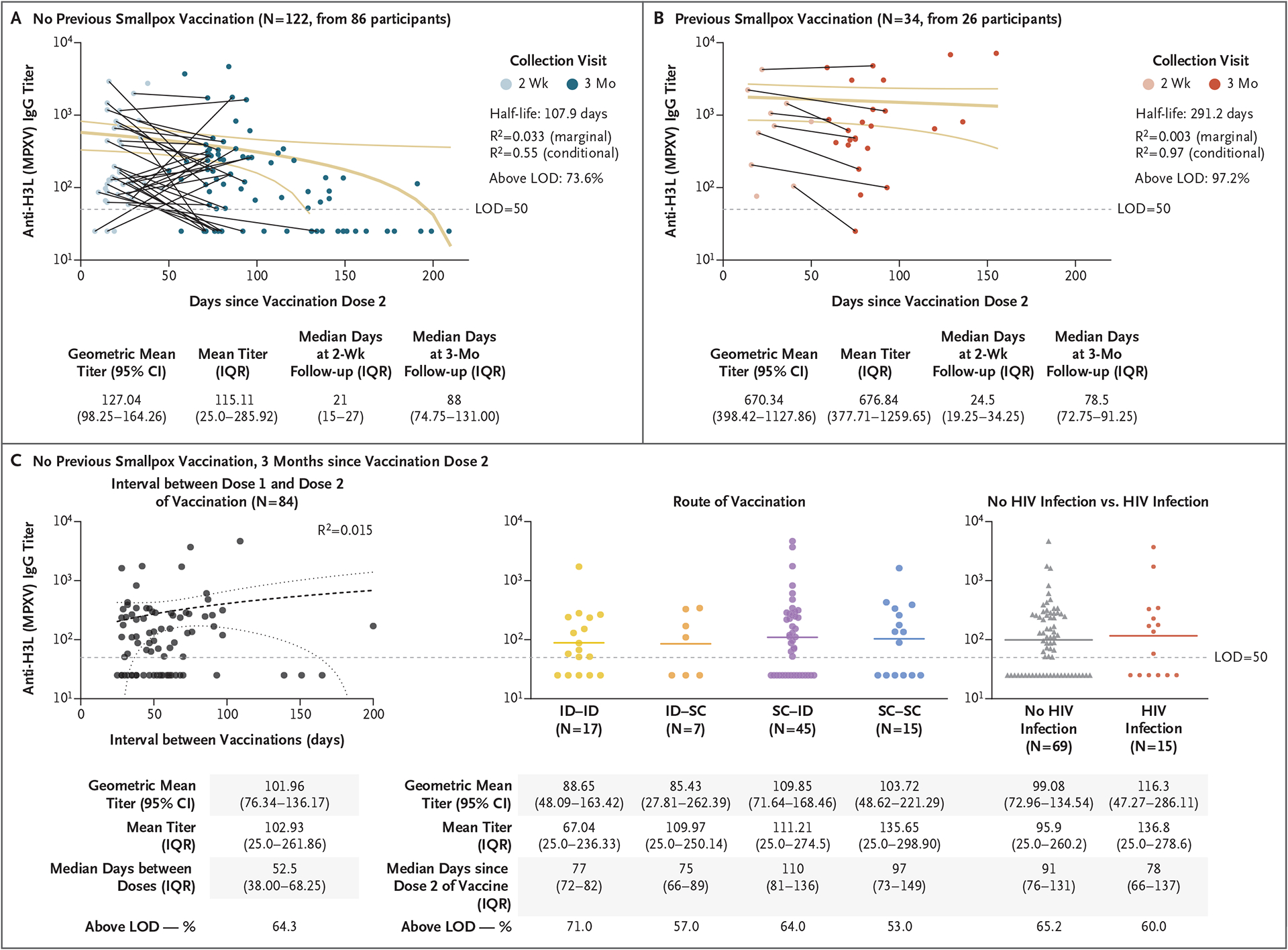
Shown are antibody titers among study participants who had received two doses of the MVA-BN vaccine among those without a history of smallpox vaccination (Panel A) and among those with a history of smallpox vaccination (Panel B). The marginal R2 is the proportion of variance explained by the fixed effects relative to the overall variance, and the conditional R2 is the proportion of variance explained by both fixed and random effects relative to the overall variance. Three months after the second dose of vaccine in participants who had not received previous smallpox vaccination, there was no indication of decreased titers with longer intervals between the recommended two doses (Panel C, left); IgG titers were similar regardless of the route of administration (Panel C, center) or HIV status (Panel C, right). For each of the two doses, the route of administration was intradermal (ID), subcutaneous (SC), or a combination of the two routes. Confidence intervals (CI) have not been adjusted for multiplicity and should not be used for hypothesis testing. IQR denotes interquartile range, and LOD limit of detection.
