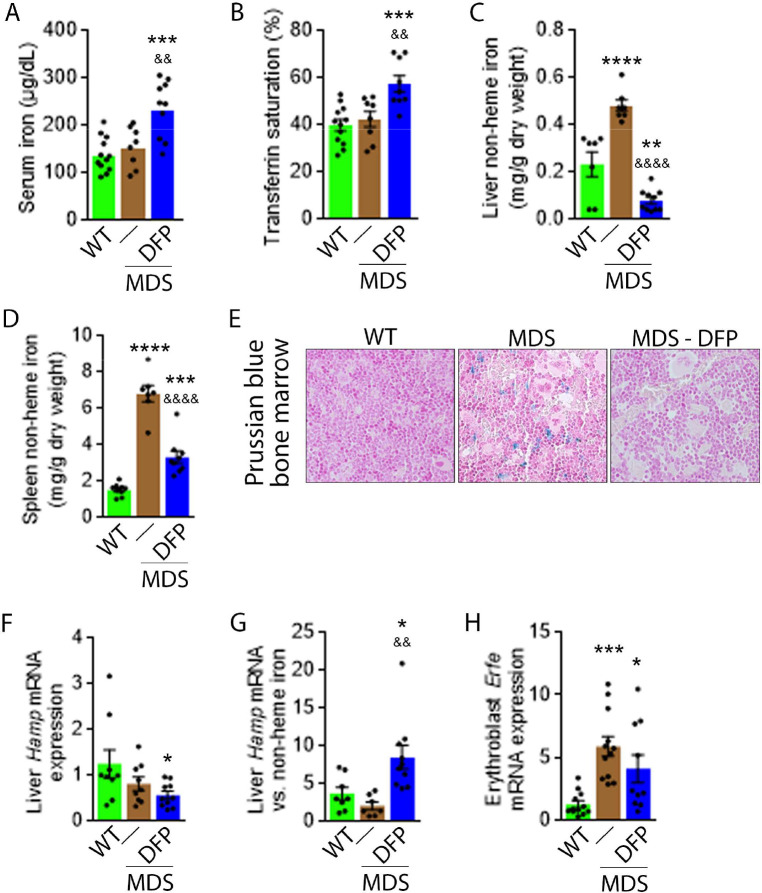
Figure 1. DFP reverses parenchymal iron overload and restores hepcidin iron responsiveness in MDS mice.
DFP results in increased serum iron (A) and transferrin saturation (B) while reducing parenchymal iron in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow (C-E). While liver Hamp mRNA expression is unchanged in WT, MDS, and DFP-treated MDS mice (F), Hamp responsiveness to iron is normalized in DFP-treated MDS mice (G) (n=7–10 mice/group). (H) DFP results in more normal Erfe mRNA expression (n=10–12 mice/group) in sorted bone marrow erythroblasts from MDS mice analyzed after 1 month of treatment. *p<0.05 vs. WT; **p<0.01 vs. WT; ***p<0.001 vs. WT; ****p<0.0001 vs. WT; &p<0.05 vs. MDS; &&p<0.01 vs. MDS; &&&&p<0.0001 vs. MDS; Abbreviations: WT = wild type; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome; DFP = deferiprone; Hamp = hepcidin; Erfe = erythroferrone.
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Erythroblast apoptosis in MDS mice.
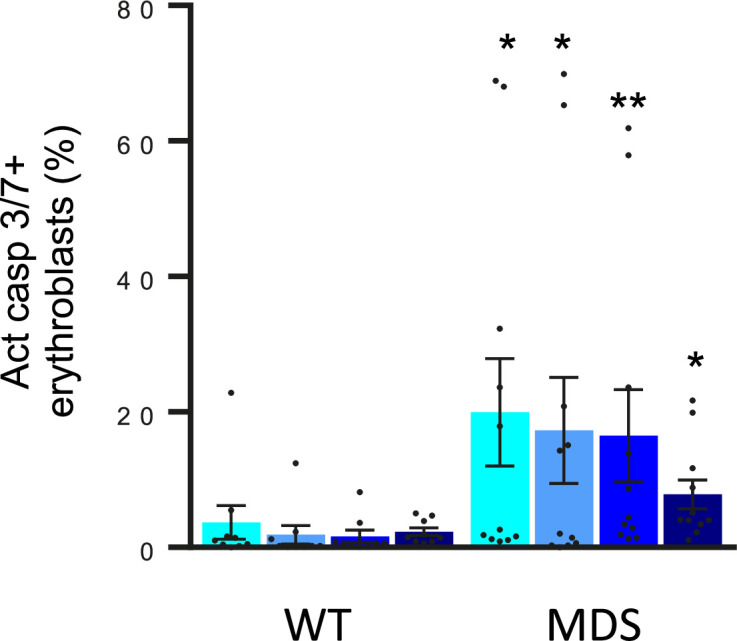
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Quantification of serum DFP concentration in DFP-treated WT and MDS mice.
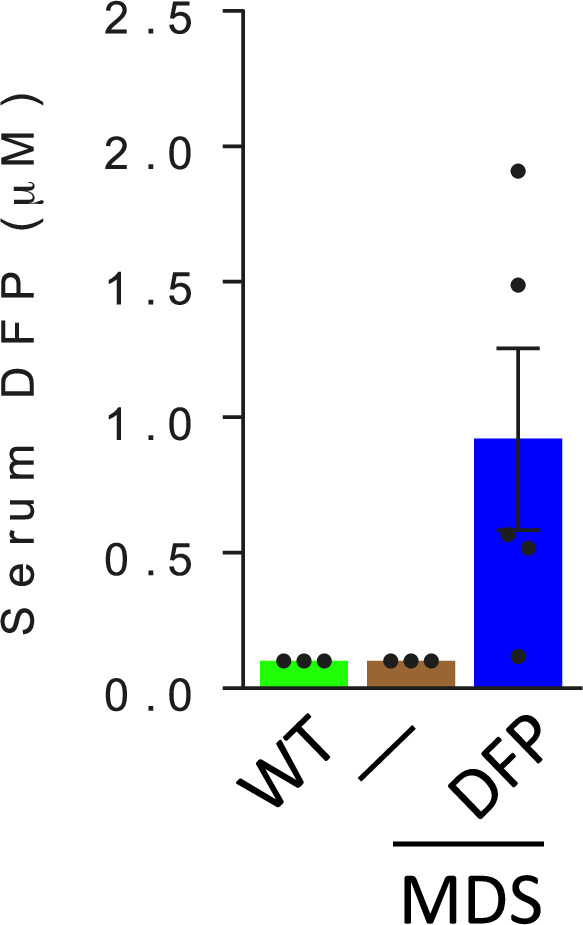
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. DFP resulted in similar effects on transferrin saturation in male and female MDS mice.
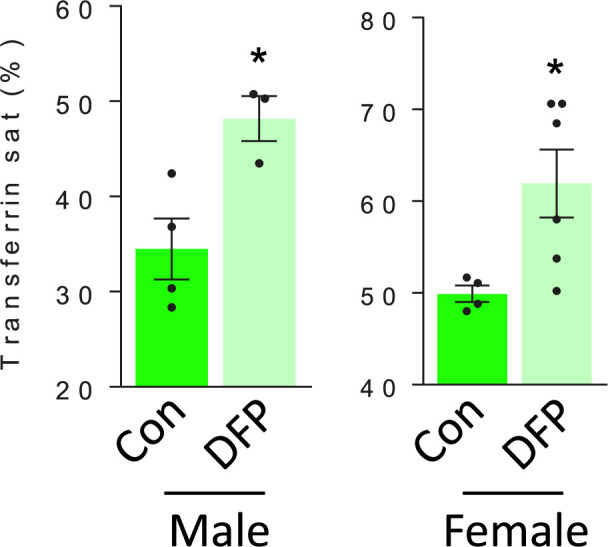
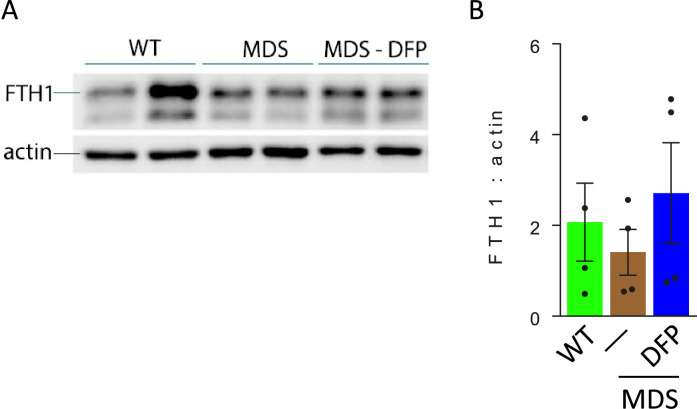
Figure 1—figure supplement 4. Bone marrow erythroblast ferritin is increased in DFP-treated MDS mice.
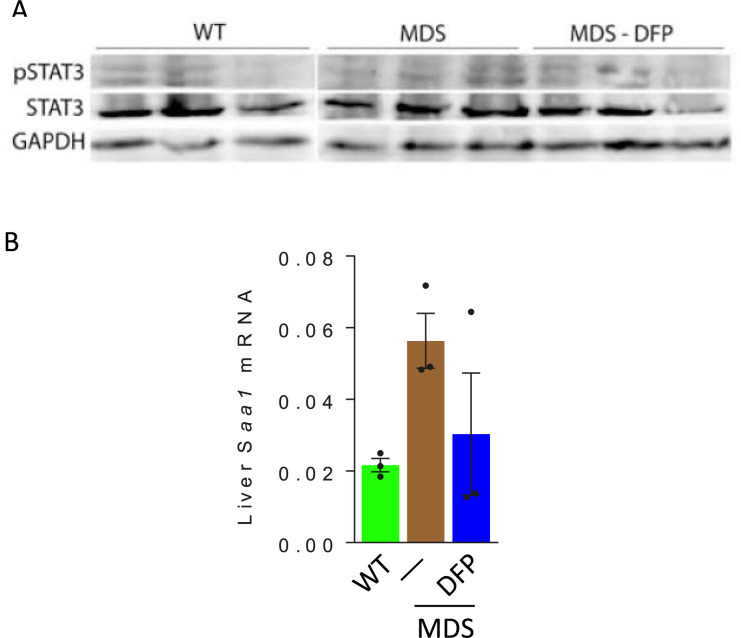
Figure 1—figure supplement 5. Effects of DFP on the liver STAT3 expression in MDS mice.
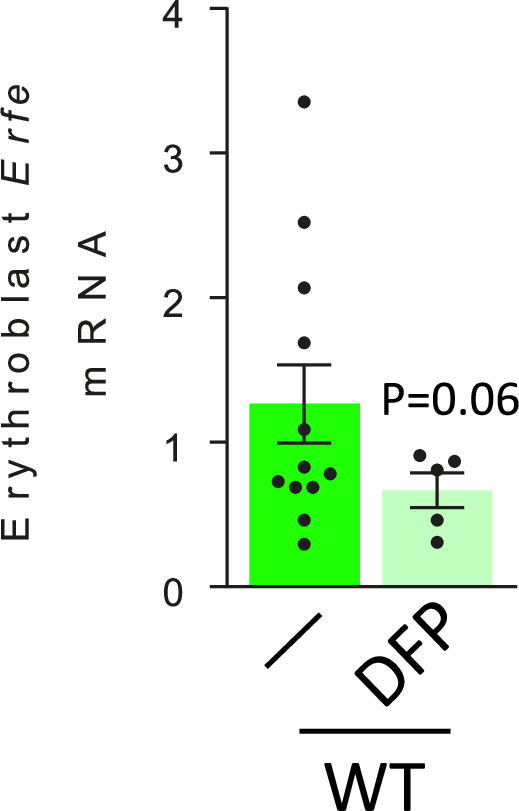
Figure 1—figure supplement 6. Effect of DFP on erythroblast Erfe expression in WT mice.