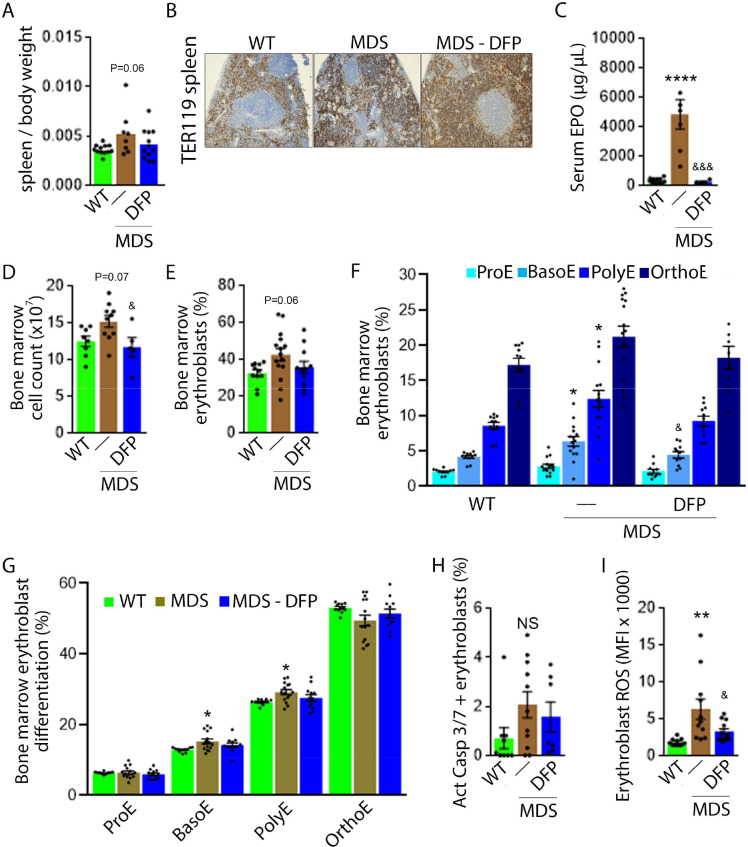
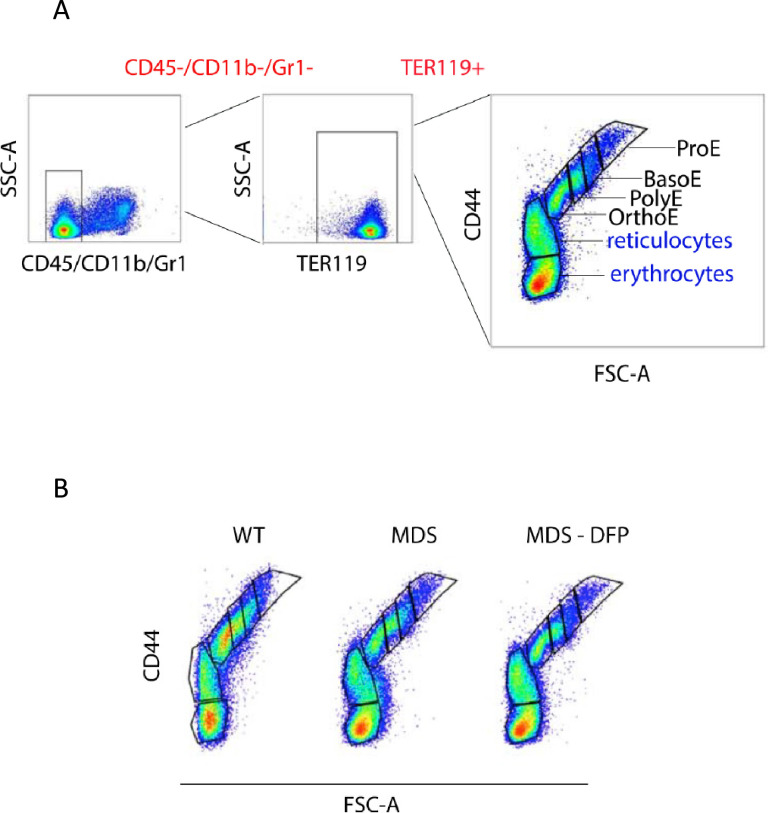
Figure 3. Expanded and ineffective erythropoiesis in MDS mice is partially reversed by DFP.
Spleen weight (n=11–12 mice/group) (A), splenic architecture (n=5 mice/group) (B), serum EPO concentration (n=5–12 mice/group) (C), bone marrow erythroblast count (n=13–15 mice/group) (D), and the total fraction of erythroblasts in the bone marrow (n=13–15 mice/group) (E) are more normal in DFP-treated MDS mice analyzed after 1 month of treatment. The fraction of all stages of terminal erythropoiesis is increased in MDS relative to WT mice in BasoE and PolyE stages and decreased in DFP-treated relative to untreated MDS mice in BasoE stages (n=13–15 mice/group) (F). Erythroblast differentiation in the bone marrow, decreased in MDS relative to WT, is normalized in DFP-treated relative to untreated MDS mice (n=13–15 mice/group) (G). In addition, erythroblast apoptosis, as measured by activated caspase 3/7, is unchanged in DFP-treated MDS mice (n=7–11 mice/group) (H). Finally, erythroblast ROS is decreased in DFP-treated relative to untreated MDS mice (n=11–12 mice/group) (i) analyzed after 1 month of treatment. *p<0.05 vs. WT; **p<0.01 vs. WT; ****p<0.0001 vs. WT; &p<0.05 vs. MDS; &&&p<0.001 vs. MDS; Abbreviations: WT = wild type; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome; DFP = deferiprone; EPO = erythropoietin; Act casp 3/7 = activated caspase 3 and 7; ROS = reactive oxygen species; ProE = pro-erythroblasts; BasoE = basophilic erythroblasts; PolyE = polychromatophilic erythroblasts; OrthoE = orthochromatophilic erythroblasts; NS = not significant.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. DFP resulted in similar effects on erythropoiesis in male and female myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) mice.
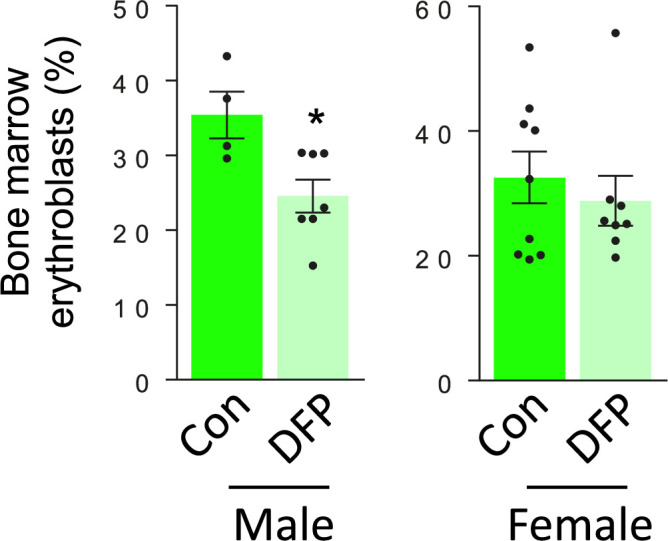
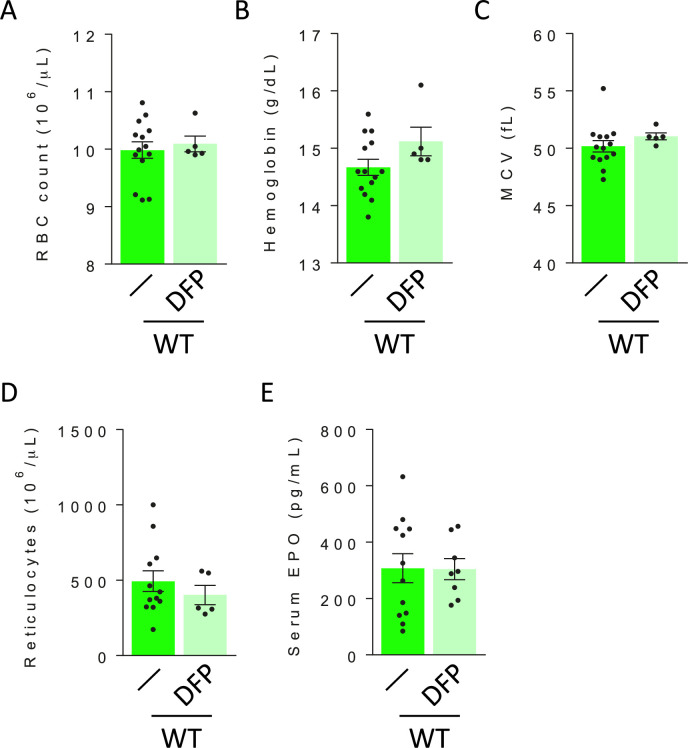
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. DFP has no effect on circulating red blood cell parameters and serum erythropoietin in WT mice.
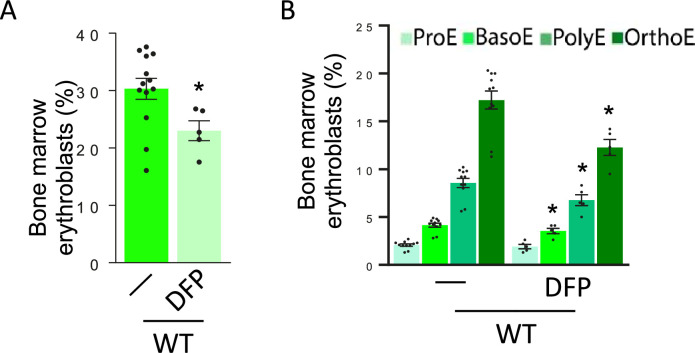
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Effect of DFP on erythropoiesis in WT mice.
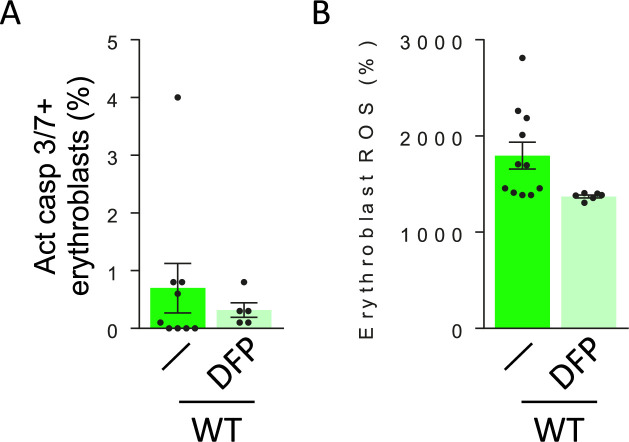
Figure 3—figure supplement 4. DFP has no effect on erythroblast apoptosis and reactive oxygen species in WT mice.
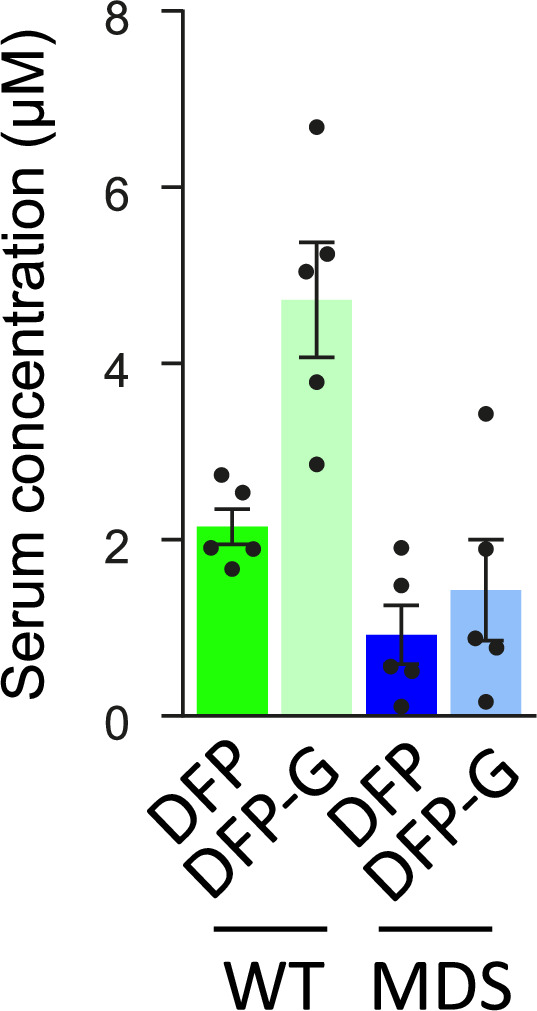
Figure 3—figure supplement 5. Quantification of serum DFP-glucuronide concentration in DFP-treated WT and MDS mice.