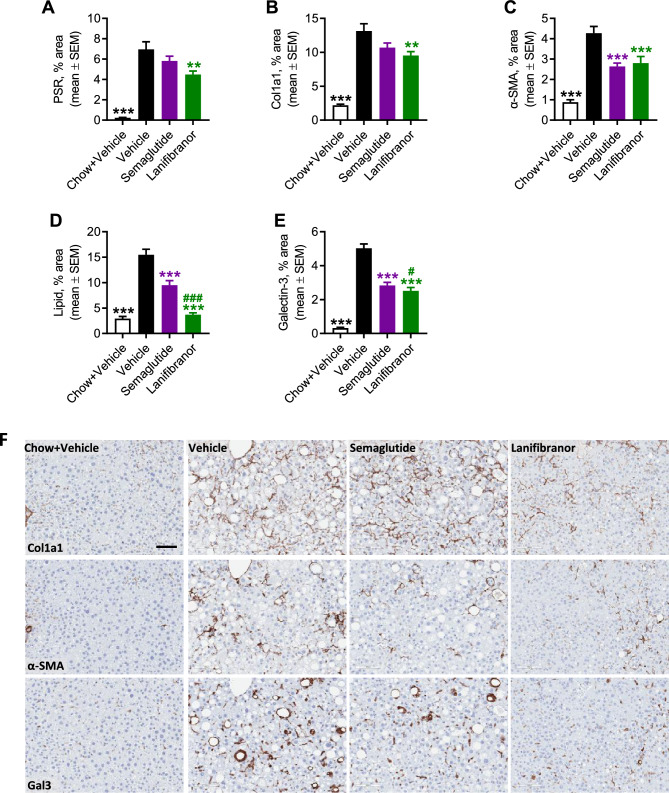
Figure 6.
Semaglutide and lanifibranor differentially improves quantitative histological markers of fibrosis, steatosis and inflammation in GAN DIO-NASH-HCC mice. GAN DIO-NASH-HCC mice with biopsy-confirmed NASH and fibrosis were administered (QD) vehicle (SC), semaglutide (30 nmol/kg, SC) or lanifibranor (mg/kg, PO) for 14 weeks (n = 15–16 per group). Treatment was initiated after 54 weeks of GAN diet feeding. Mice were stratified/randomized to treatment according to severity of NASH (NAS ≥ 5) and fibrosis (fibrosis stage F3) assessed 4 weeks before treatment start. Chow-fed mice receiving (QD) saline vehicle for 14 weeks (Chow + Vehicle) served as normal controls (n = 10). (A–E) Proportionate (%) area of (A, B) Fibrosis (PSR, Col1a1), (C) α-SMA (fibrogenesis marker), (D) lipids, and (E) inflammation (galectin-3). (F) Representative photomicrographs illustrating reduced fibrosis (Col1a1), fibrogenesis (α-SMA) and inflammation (galectin-3) after semaglutide and lanifibranor treatment. Only lanifibranor reduced quantitative levels of fibrosis (PSR, Col1a1). Scale bar, 100 µm. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle-dosed GAN DIO-NASH mice; #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 versus semaglutide (Dunnett’s test one-factor linear model).