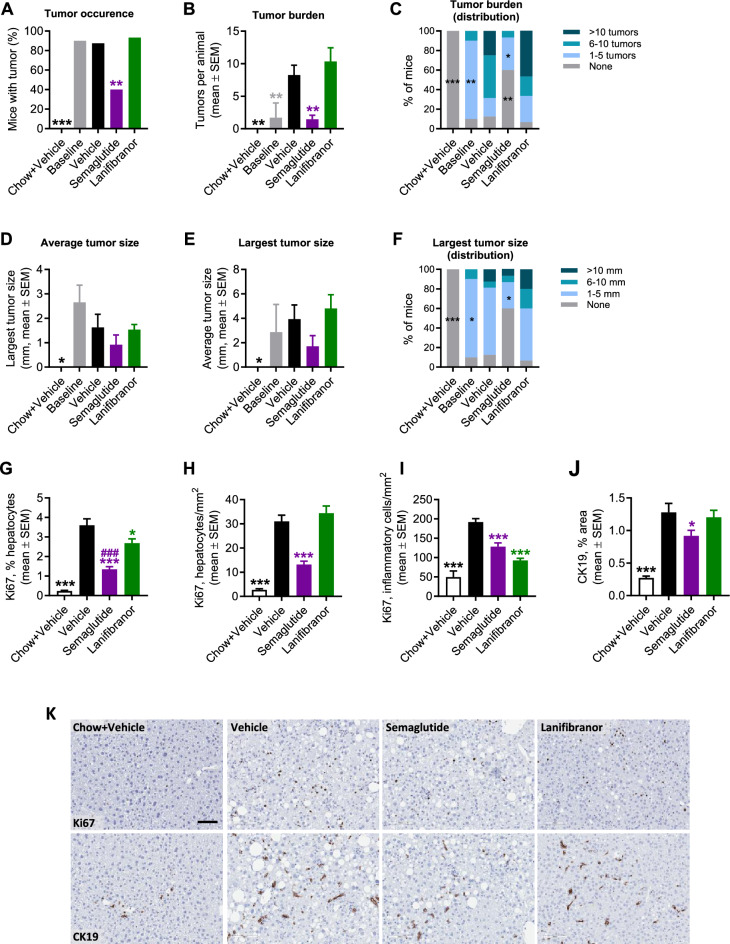
Figure 7.
Semaglutide, but not lanifibranor, reduces tumor burden in GAN DIO-NASH-HCC mice. GAN DIO-NASH-HCC mice with biopsy-confirmed NASH were administered (QD) vehicle (SC), semaglutide (30 nmol/kg, SC) or lanifibranor (mg/kg, PO) for 14 weeks (n = 15–16 per group). Treatment was started after 54 weeks of GAN diet feeding. Chow-fed mice receiving (QD) saline vehicle for 14 weeks (Chow + Vehicle) served as normal controls (n = 10). Baseline HCC burden was assessed in a satellite group of GAN DIO-NASH-HCC mice (n = 10) after 54 weeks of GAN diet feeding. (A) Tumor occurence. (B) Tumor burden. (C) Distribution of tumor burden. (D) Average tumor size (mm). (E) Largest tumor size (diameter, mm). (F) Distribution of largest tumor size. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle-dosed GAN DIO-NASH mice (Dunnett’s test one-factor linear model). (G–I) Ki67 staining of hepatocytes (relative number, %; area, mm2) and inflammatory cells (area, mm2). (J) Proportionate (%) area of CK19 staining. (K) Representative Ki67 and CK19 stainings illustrating treatment effects on Ki67 and CK19 staining. Scale bar, 100 µm. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus vehicle-dosed GAN DIO-NASH mice; ###p < 0.001 versus lanifibranor (Dunnett’s test one-factor linear model).