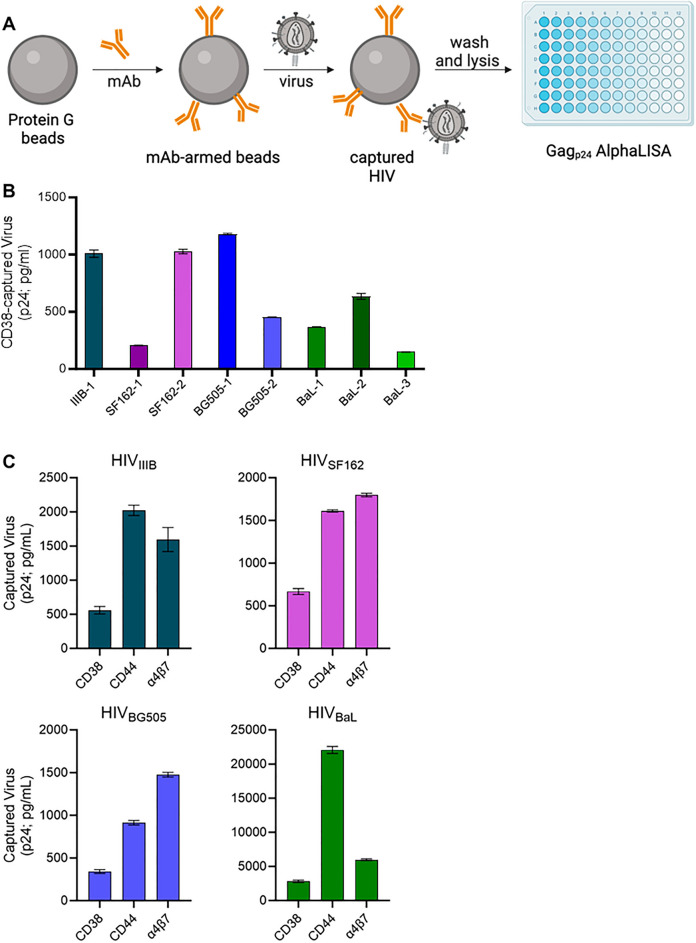
Figure 4.
Bead-based capture of HIV virus stocks using an anti-CD38 antibody. (A) A schematic representation of the bead-based virion capture assay. Protein G coated magnetic beads are armed with the antibody (mAb) against the protein to be detected on the viral surface. The virus is incubated with the antibody-armed beads for 2 h at room temperature to allow virus capture, followed by washing and lysis of bead-bound (i.e., captured) virus. The amount of virus captured via each mAb is quantified by Gag p24 AlphaLISA performed on viral lysates. (B) Virion capture assays were performed on equal volumes of eight independent virus stocks of HIV isolates (BaL, IIIB, BG505, SF162) grown in different PBMC donors. The numbering of isolates indicates a distinct viral stock produced in a different PBMC donor for the same viral isolate (i.e., BaL-1, BaL-2, and BaL-3 are the same BaL isolate grown in 3 different PBMC donors). Bead-associated virus was lysed and HIV-1 p24 Gag was quantified using p24 AlphaLISA as an indicator of the amount of virus capture. Background levels of capture achieved with an isotype-matched control antibody were subtracted from all data shown. Levels of CD38 capture displayed are significantly higher than isotype capture (paired t-test; p = 0.003). (C) Virion capture assays were performed with immunomagnetic beads armed with antibodies against CD38, CD44 or integrin β7 with each virus isolate (BaL, IIIB, BG505, SF162). In parallel, we assessed the levels of background capture as measured with an isotype control, and these control values were subtracted from the capture data before graphing. Levels of CD38 capture displayed are significantly higher than isotype capture (paired ANOVA; p = 0.004). The mean ± SD are generated from independent virus stocks tested in duplicate.