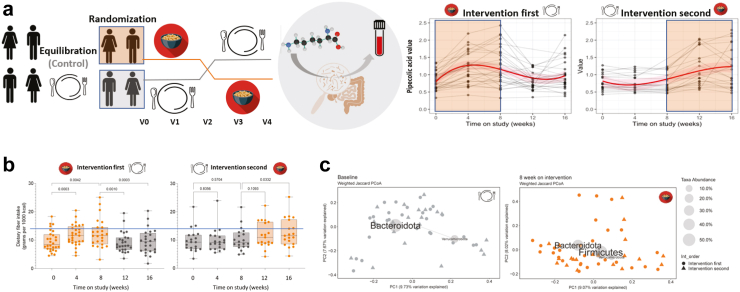
Fig. 2.
The BE GONE Trial tested the effect of cooked dry bean addition and depletion within the participant's usual diet. a. Study design, Left to Right: To establish the basal diet and microbiome and introduce study procedures prior to randomization, eligible and consented individuals began the equilibration/run-in. Participants who completed the run-in were randomized to begin the dry bean intervention or to continue the usual diet control for 8 weeks. The intervention diet consisted of adding ½ cup (1 serving) of cooked, canned navy beans to their usual diet over a 2-week ramp-up period followed by 1 cup (2 servings) per day for an additional 6 weeks. At week 8, participants who completed the intervention diet immediately crossed over to the control (usual diet without beans) and vice versa for a total of 5 in-person visits every 4 weeks with stool and fasting blood collection. The primary outcome focused on changes in stool 16S rRNA gene profiles and blood metabolites/markers. Trends in pipecolic acid, a specific marker of dry bean intake and microbiome-derived metabolite of lysine, paralleled the addition and the depletion of cooked navy beans within the usual diet, providing an objective measure of compliance. b. Total dietary fiber intake within the usual diet from multiple 24-h recalls collected across the intervention sequence showed that majority of participants remained below the adequate intake threshold for U.S. adults of 14 g per 1000 kcal [means, medians, interquartile range and outliers presented with p-values comparing intervention (orange) and control (gray) periods]. Within person change in total dietary fiber intake for the 8-week on-intervention period for both groups combined, linear mixed effect (LME) estimate and 95% CI: 0.22 (0.10, 0.35) interpreted as slope above 0 by generalized linear mixed models (proc glimmix, SAS 9.4) with random intercept in natural log scale. c. Beta diversity by weighted Jaccard similarity/distance across randomization groups visualized as PCoA biplots with the most abundant phylum-level taxa at baseline and 8 weeks post-intervention in the full trial cohort (n = 48).