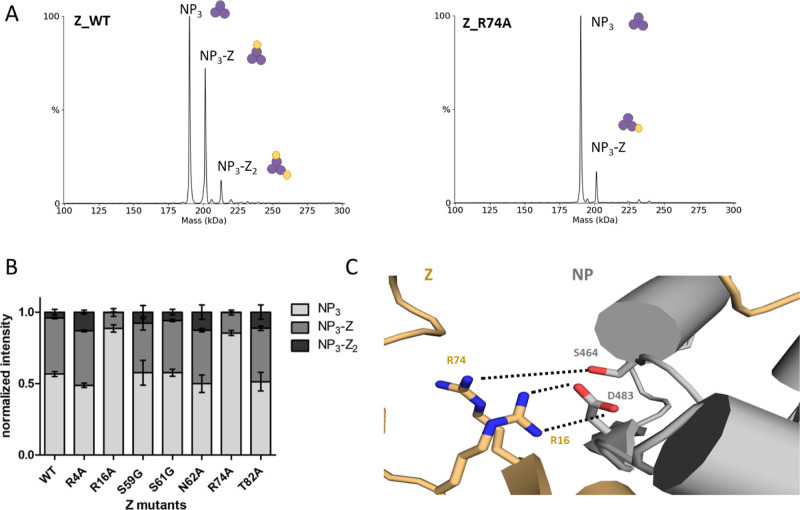
Figure 5.
Z mutant screening identifies important residues for the NP-Z interaction. The different Z mutants were recombinantly expressed and purified. (A) nMS screening of the Z mutants together with NP (6 μM) in a 1:3 (NP/Z) molar ratio in a 150 mM ammonium acetate solution at pH 7.5. (B) Sum of the intensities of every mass species of one measurement was normalized to 1. The normalized intensities for every measurement were plotted. Error bars represent standard deviation of at least three independent measurements. Measurements with the mutants R16A and R74A show reduced abundance of NP-Z complex species compared to wildtype (WT). (C) Detailed closeup to the Z residues R74 and R16 in the AlphaFold Multimer model. Z residues R74 and R16 are in close proximity to NP-S464 and NP-D483, respectively.