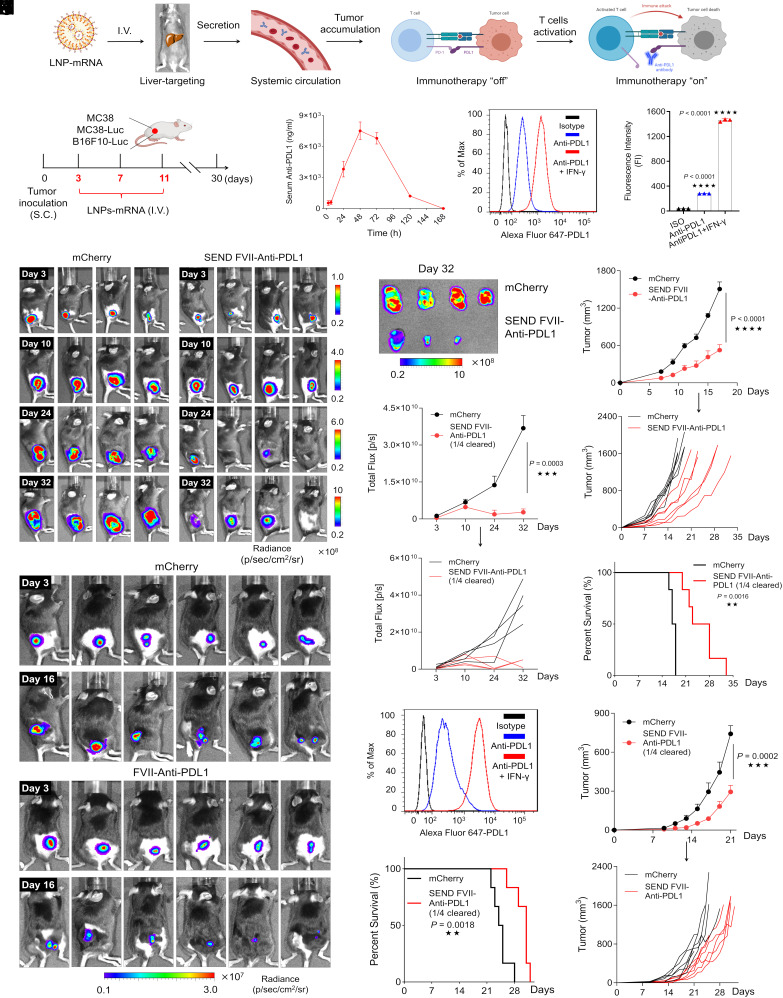
Fig. 5.
SEND FVII-anti-PDL1 LNPs reduce tumor burden and extend survival in vivo. (A) Scheme of anti-PDL1 antibody production and tumor immunotherapy. (B) Scheme of experimental design utilizing MC38, MC38-Luc, and B16F10-Luc xenograft mice models. (C) Pharmacokinetic profile of serum anti-PDL1 antibody secretion after single dosing with SEND mRNA LNPs. Mice were I.V. injected with a dose of 0.5 mg/kg mRNA. Serum was collected at different time points, and anti-PDL1 was detected by ELISA. (D) Representative PD-L1 expression on the membrane surface of MC38 cells determined by flow cytometry. (E) Luminescence images of MC38-Luc tumors at different time points captured by IVIS. (F) Luminescence images of isolated MC38-Luc tumors at day 32. (G) Quantified luminescence signal in MC38-Luc tumor area at different time points. (H) Tumor growth of the native MC38 model and (I) mice survival during treatments by mRNA formulations. (J) Luminescence images of B16F10-Luc tumors on day 3 and day 16 treated with different formulations. (K) Representative PDL1 expression on the membrane surface of B16F10-Luc cells determined by flow cytometry. (L) Tumor growth of B16F10-Luc model and (M) mice survival during treatments by mRNA formulations. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and ****P < 0.0001).