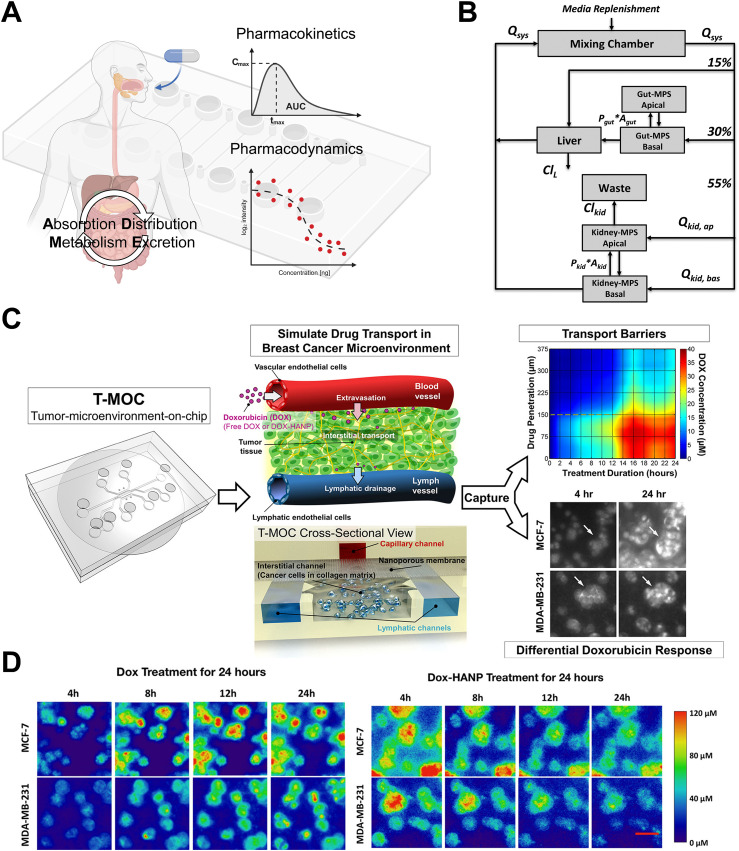
FIG. 3.
Employment of MPS models for assessing PKPD. (a) A schematic illustrates drug PKPD based on absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Created with BioRender. (b) Multi-functional scaling for muti-organ MPS design was established to optimize the integrated platforms mimicking in vivo drug exposures. Adapted with permission from Maass et al., Integr. Biol. 9(4), 290–302 (2017). Copyright 2017 Oxford University Press. (c) Utilizing the tumor-microenvironment on-chip (T-MOC) platform to emulate drug transport within the breast cancer microenvironment, enabling the study of drug penetration and accumulation. Adapted with permission from Ozcelikkale et al., J. Controlled Release 266, 129–139 (2017). Copyright 2017 Elsevier B.V. (d) Comparison of the distinct drug accumulation patterns of doxorubicin (Dox) and Dox-loaded hyaluronic acid nanoparticles (Dox-HANPs) within the breast cancer T-MOC platform. Reprinted with permission from Shin et al., Mol. Pharm. 13(7), 2214–2223 (2016). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.