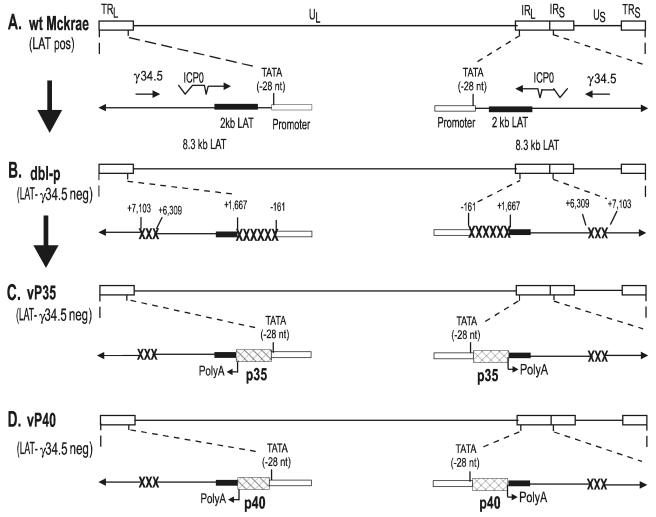
FIG. 1.
Construction and structure of the vP35 and vP40 recombinant viruses. (A) The top of the schematic shows the HSV-1 McKrae genome in the prototypic orientation. The rectangles labeled long terminal repeat (TRL) and long inverted repeat (IRL) represent the terminal and internal (or inverted) long repeats, whereas the rectangles labeled short terminal repeat (TRS) and short inverted repeat (IRS) represent the terminal and internal (or inverted) short repeats. Unique long (UL) and unique short (US) labels represent the long and short unique regions, respectively. The expanded presentation of part of the internal long and short repeats indicates the location and orientation of LAT and γ34.5 transcripts. The ICP0 and γ34.5 mRNA is shown for reference. The solid rectangle represents the very stable 2-kb LAT. The arrow at −28 indicates the LAT TATA box. (B) LAT-γ34.5-null mutant (dbl-p) virus is a mutant of HSV-1 strain McKrae in which 1.8 kb of LAT (nucleotides −161 to +1667) and 0.9 kb of γ34.5 (nt +6309 to +7103) have been deleted (49). The deleted regions are indicated by “XXXXXX” and “XXX.” (C) vP35 was constructed from parental virus by homologous recombination between parental virus DNA and a plasmid containing the complete LAT promoter and the entire structural IL-12p35 gene [including its 3′-poly(A) signal] as described in Materials and Methods. (D) vP40 was constructed similar to vP35 except recombination occurred between parental virus DNA and a plasmid containing the IL-12p40 gene.