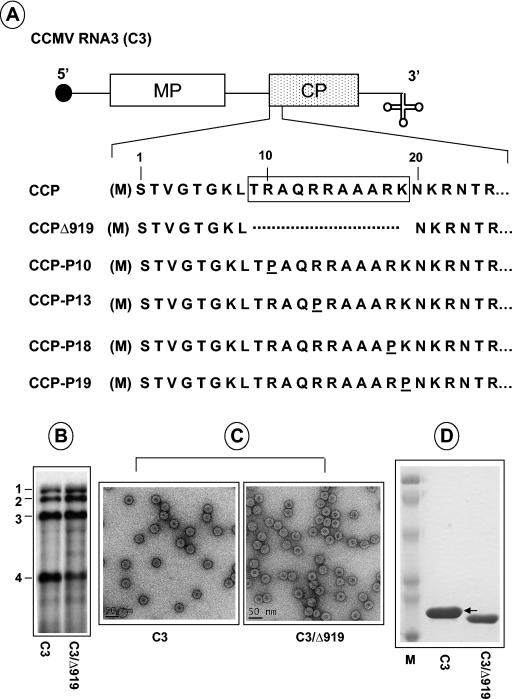
FIG. 1.
Characteristics of CCMV CP variants. (A) The structure of C3 is shown, with noncoding sequences represented as single lines and MP and CP genes shown as open and stippled boxes, respectively. A filled circle at the 5′ end and a cloverleaf at the 3′ end represent cap and tRNA-like structures, respectively. The first 25 N-proximal amino acids are shown, and the boxed region represents the N-terminal ARM conserved among plant and nonplant viruses. In CCMV, the initiating methionine (enclosed in parenthesis) is removed, and the resultant N-terminal serine is acetylated in the mature CP (21). In variant C3/Δ919, the deletion of the ARM region, located between amino acids 8 and 20, is indicated by a broken line. In variants C3/P10, C3/P13, CP/P18, and C3/CP19, arginine residues located at positions 10, 13, 18, and 19, respectively, are replaced by a proline residue. (B) Replication competence of C3/Δ919 in protoplasts. Protoplasts were transfected with WT C1 and C2 and either WT C3 or C3/Δ919. After a 24-h incubation, total RNA was isolated and subjected to Northern blot analysis. The positions of four WT CCMV RNAs are shown to the left. (C) Electron microscopy of purified virions. Virions were purified from symptomatic leaves, applied to glow-discharged carbon-coated copper grids and negatively stained with 1% uranyl acetate prior to viewing under an electron microscope. Prior to application of the sample onto the grids, WT samples were diluted 1:10 while the Δ919 samples remain undiluted. (D) Analysis of viral capsid protein. Purified virions resulting from infections of either WT C3 or C3/Δ919 were suspended in sample buffer, boiled for 5 min, and subjected to SDS-10% PAGE. The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue prior to photography. An arrow indicates the position of WT CP. Lane M, molecular weight marker proteins.