FIG. 3.
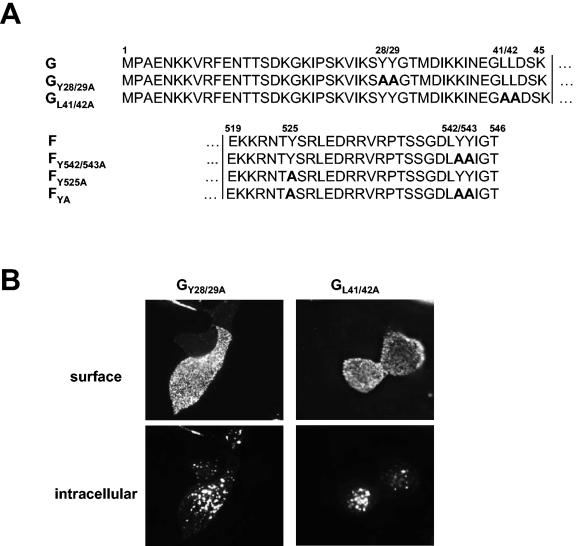
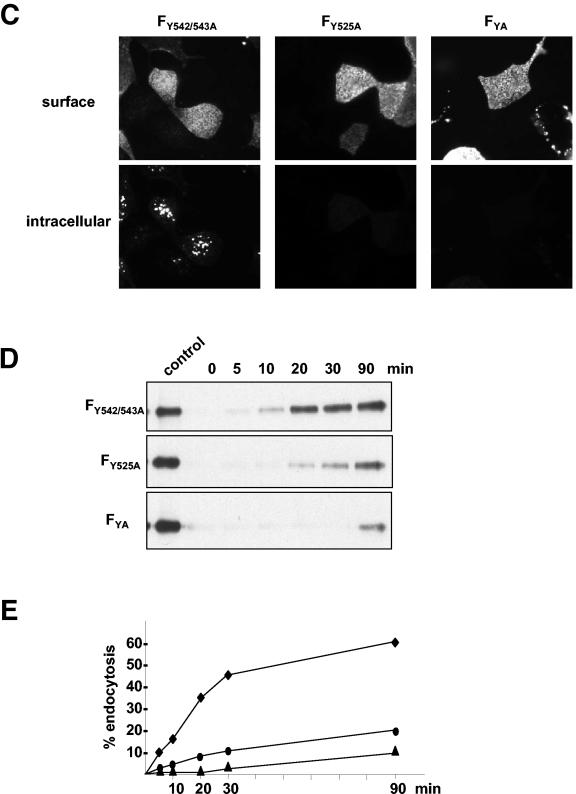
Internalization of F and G proteins with mutations in the potential endocytosis signals. (A) Sequences of the cytoplasmic domains of wild-type and mutant G and F proteins. The numbers above the sequences indicate the amino acid positions. Amino acid sequences are shown in a single-letter code; boldface letters indicate exchanged amino acid residues. The vertical lines separate the transmembrane domains from those predicted to be in the cytoplasm. (B and C) Antibody uptake analysis of mutant G (GY28/29A and GL41/42A) (B) and mutant F (FY542/543A, FY525A, and FYA) (C) proteins was performed as described in the legend to Fig. 2A. (D) Endocytosis of mutant F proteins (FY542/543A, FY525A, and FYA) was determined after surface biotinylation and MESNA reduction as described in the legend to Fig. 2B. (E) The rates of internalization were determined by plotting the percentages of endocytosed FY542/543A (⧫), FY525A (•), and FYA (▴) proteins as functions of the times that the cells were incubated at 37°C. (F) The total amount of surface-expressed wild-type (F) and mutant F (FY542/543A, FY525A, and FYA) proteins was determined by the surface biotinylation of 2 × 106 cells at 30 h posttransfection. After cell lysis, the F proteins were immunoprecipitated and detected as described in the legend to Fig. 2A.