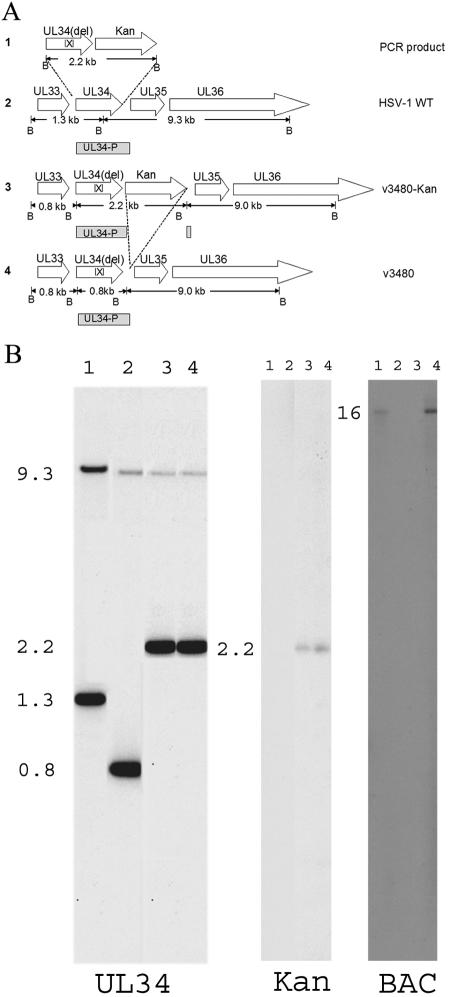
FIG. 4.
(A) Schematic diagram of steps involved in the construction of a virus bearing a UL34 gene lacking codons 137 to 181. Line 1, sequences within a 2.2-kb PCR product containing the UL34 gene lacking codons 137 to 181 and a gene encoding kanamycin resistance (Kan) flanked by Frt recombination sites (not shown), with 50 bp of sequence homologous to regions flanking UL34 in wild-type viral genomes and BamHI restriction sites. Line 2, wild-type HSV-1 sequences containing UL34 and schematic diagram of the UL34 probe (UL34-P, gray rectangle) used to hybridize to DNA sequences, as shown in panel B. The lengths of the expected DNA fragments are indicated in kilobase pairs and are delimited by BamHI (B) sites. Line 3, genome of the UL34 mutant virus v3480-Kan after homologous recombination within the 50-bp sequences flanking the Kanr gene and UL34. The sizes of the expected BamHI fragments are indicated in kilobase pairs below the rectangles. Line 4, genome of the UL34 mutant virus v3480 after deletion of the kanamycin resistance gene at the Frt sites by the induction of Flp recombinase. (B) Digitally scanned image of a fluorograph of viral DNAs probed with radiolabeled DNAs. Viral DNAs were purified, digested with BamHI, and electrophoretically separatedin a 1% agarose gel. The DNAs were transferred to nitrocellulose and probed with [α-32P]dCTP-labeled UL34 (schematically diagramed as UL34-P in panel A), the gene encoding kanamycin resistance, or the BAC vector sequence. Lanes 1, HSV-BAC; lanes 2, v3480 DNA; lanes 3, v3480-Kan DNA; lanes 4, v3480-Kan-BAC DNA. The numbers indicate the sizes of the DNA fragments in kilobase pairs.