Figure 6.
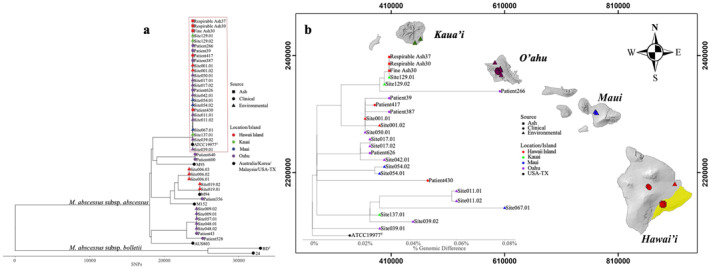
Whole genome sequence analyses reveal phylogenetically related M. abscessus in Kīlauea ash, the local environment, and respiratory isolates from individuals on neighboring islands. (a) Phylogenetic relationships between Kīlauea ash‐derived M. abscessus (red squares), environmental isolates (triangles), and respiratory isolates (circles) from individuals residing in Hawai'i. The red rectangle highlights genetically similar (>99.999%) isolates. (b) Phylogenetic tree of isolate genomes within the highlighted box in “A” show the % genomic differences between isolates are <0.001% single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (36 SNPs) cross the entire core genome comprising >4M nucleotide positions. These M. abscessus are mapped onto their island of origin. Volcanic ash isolates from Hawai'i Island are genetically identical to environmental and respiratory M. abscessus from other islands. The geographic area of the Kīlauea Volcano is highlighted in yellow. The Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System (zone 5) was used for the map; values in meters (m) are indicated. The superscript “T” designates that the isolate is a type strain for a given taxon.
