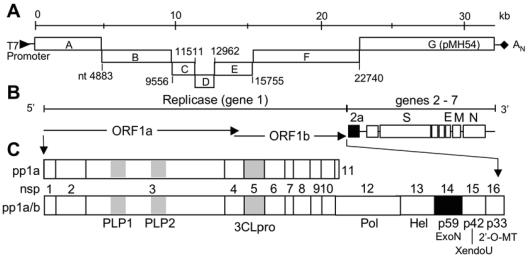
FIG. 1.
MHV genome organization, proteins, and genome cDNA fragments. (A) The MHV reverse genetics system divides the genome into seven cDNA fragments with a T7 promoter at the beginning of fragment A and poly(A) tail at the end of the fragment G (pMH54). The junction of the fragments is indicated by nucleotide number. (B) The genome consists of seven genes. The replicase gene comprises the first 22 kb. Genes 2 to 7 are translated from subgenomic mRNA species (not shown). The relative locations of coding regions for the structural proteins S, E, M, and N are shown, as is the coding region for the group-specific ORF 2a 30-kDa protein. (C) The ORF 1a and frameshifted ORF 1a/b fusion polyproteins are depicted (pp1a and pp1ab, respectively). The protein domains of the replicase polyprotein are indicated by nonstructural protein number (nsp1 to 16) and by confirmed or predicted functions: PLP1 and 2, papain-like proteinases; 3CLpro, 3C-like proteinase; Pol, putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; Hel, helicase; ExoN, putative exonuclease; XendoU, putative poly(U)-specific endoribonuclease; 2′-O-MT, methyltransferase. Proteins with substitutions are shown as black rectangles.