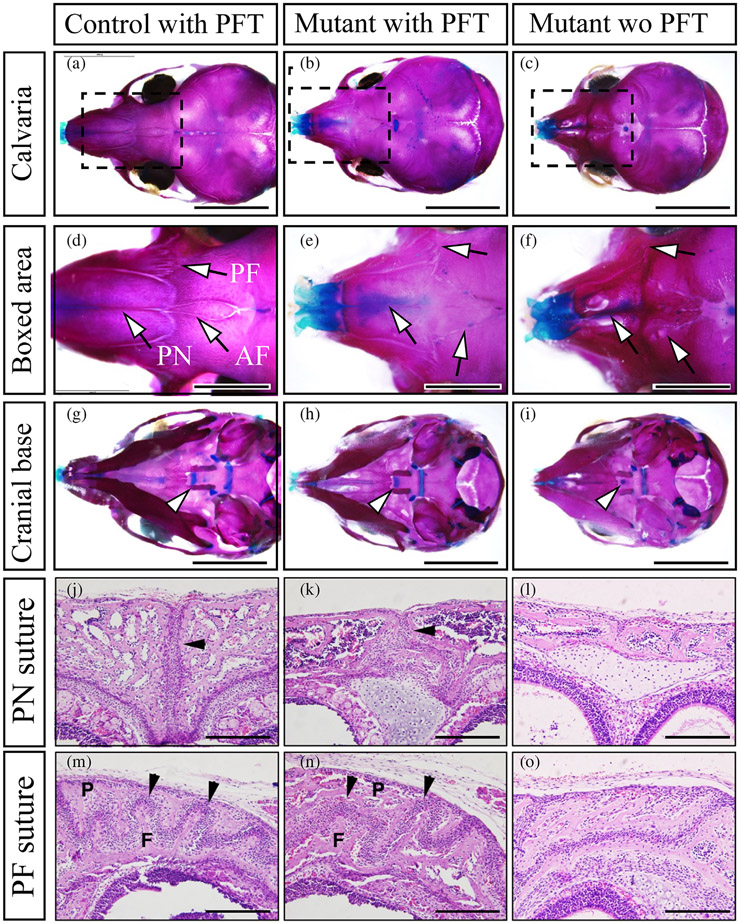
FIGURE 5.
Inhibition of p53 during early to late embryonic stage partially rescued the premature fusion of cranial sutures in P0-Cre;caBmpr1a mice. Pifithrin-α (PFT), an inhibitor for p53, was injected to the pregnant mice from embryonic day 8.5 (E8.5) to E18.5, then the skulls of control and P0-Cre;caBmpr1a mice were stained with alizarin red and alcian blue (Skeletal preparation) following the pups were harvested at postnatal day 10. (a–c) Cranial sutures in control mice with PFT (control with PFT), P0-Cre;caBmpr1a mice with PFT (mutant with PFT), and P0-Cre;caBmpr1a mice without PFT (Mutant wo PFT) were shown. (d–f) Boxed area in a–c were enlarged. Arrows indicated the anterior frontal suture (AF), premaxilla-frontal suture (PF), and posterior nasal suture (PN), respectively. (d–f) Synchondroses in control with PFT, Mutant with PFT, and Mutant without PFT were shown. Arrowheads indicated intersphenoidal synchondrosis (ISS). (j–o) Histological observations for the PN suture (j–l) and the PF suture (m–o) by hematoxylin and eosin staining were done. Black arrows indicated patent sutures (2 out of 5 pups showed the partial restoration). F and P in the PF suture mean frontal bones and posterior bones. Scale; 5 mm (a–c, g–i), 2 mm (d–f), 200 μm (j–o).