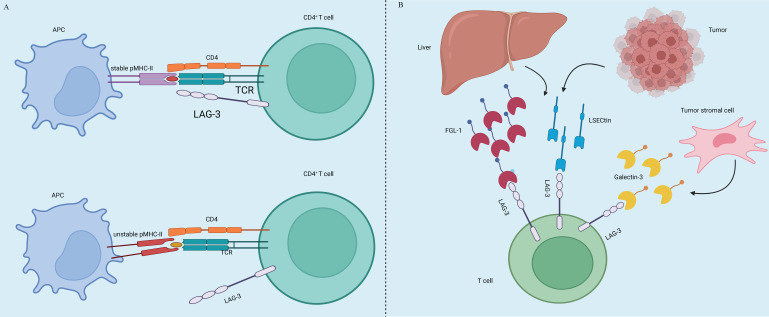
Figure 2.
LAG-3 expression and ligands. (A) LAG-3 is not initially present on primary T cells but can be induced upon antigen stimulation on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. It is also expressed in a particular subset of CD4+ T cells with suppressive capabilities. LAG-3 can selectively bind to stable pMHCII7, distinguishing the conformation of pMHCII11. (B) Additionally, FGL1 protein is a significant functional ligand for LAG-3. Upregulation of FGL1 expression by tumor cells can regulate the inhibitory function of LAG-3, thereby affecting T cell immune activity 12. Furthermore, Galectin-3 and LSECtin can interact with the glycans on LAG-3 9, 13.