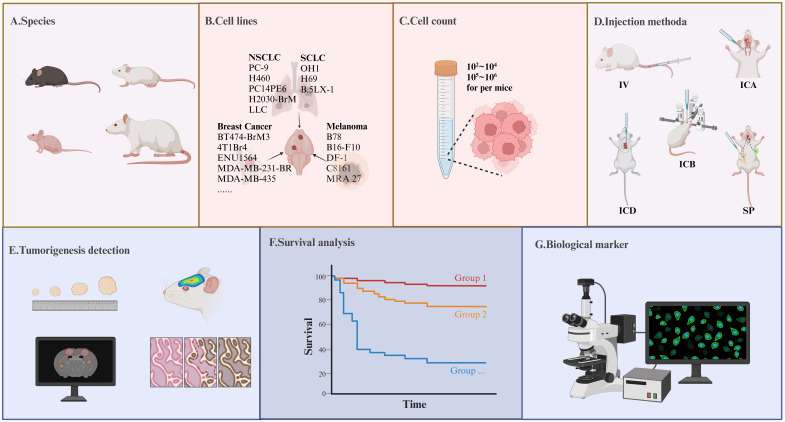
Figure 2.
Precautions in Model Construction and Detection Indicators in the AM-BM. (A-D) Several key parameters significantly influence the tumor formation rate during AM-BM model development. (A) Species including C57BL/6 mice, SCID mice, BALB/c nude mice, and rats are frequently utilized in AM-BM studies. (B) Various cell lines, such as lung cancer (H2030-BrM, PC-9-BrM3), breast cancer (BT474-BrM3, 4T1Br4), and melanoma cell lines (B16-F10, B78), are commonly employed for AM-BM establishment. (C) The quantity of injected cells is a critical determinant of successful model construction and the optimal time window for treatment. (D) Current BM modeling methods encompass intracerebral injection (ICB), intracardiac injection (ICD), internal carotid artery injection (ICA), tail vein injection (IV), and spontaneous or induced models (SP). (E-G) Common parameters assessed in in-vivo studies include: (E) Tumor lesion, tumor number, and tumor volume. (F) Survival. (G) Tumor biomarkers, such as the expression of Ki67, γH2AX, and so on.