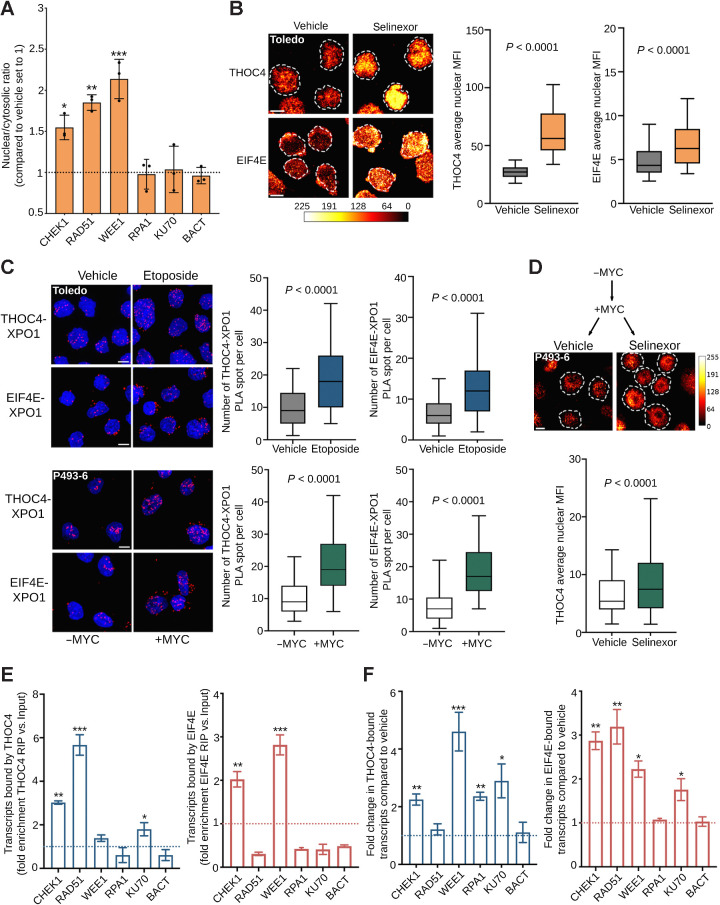
Figure 6.
XPO1 prioritizes the nuclear export of nucleoproteins carrying genotoxic stress transcripts. A, Nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio of selected DNA damage repair transcripts (i.e., CHEK1, RAD51, WEE1, RPA1, and KU70) in Toledo cells exposed to vehicle or selinexor (1 μmol/L) for 6 hours. B, Nuclear levels of THOC4 and EIF4E in Toledo cells exposed to vehicle or selinexor (1 μmol/L) for 6 hours. Left, representative images; right, quantification. The bar represents pixel intensity. C, Proximity ligation assays (PLA) of XPO1-THOC4 and XPO1-EIF4E complexes in Toledo cells exposed to vehicle or etoposide for 6 hours (top) and in P493–6 B-cells with or without MYC expression (bottom). D, Nuclear level of THOC4 in P493–6 B-cells after MYC induction, followed by vehicle or selinexor (1 μmol/L) for 6 hours. The bar represents pixel intensity. E, Ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation assays of DNA damage repair transcripts (i.e., CHEK1, RAD51, WEE1, RPA1, and KU70) bound by THOC4 (left) or EIF4E (right) in the nuclear fraction of Toledo cells. Data are presented as fold enrichment over input. F, Change in the amount of DNA damage repair transcripts CHEK1, RAD51, WEE1, RPA1, and KU70 (and actin as control) bound by THOC4 (left) and EIF4E (right) in Toledo lymphoma cells exposed to vehicle or etoposide for 6 hours. Data are presented as fold enrichment over vehicle (normalized by their respective inputs). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.