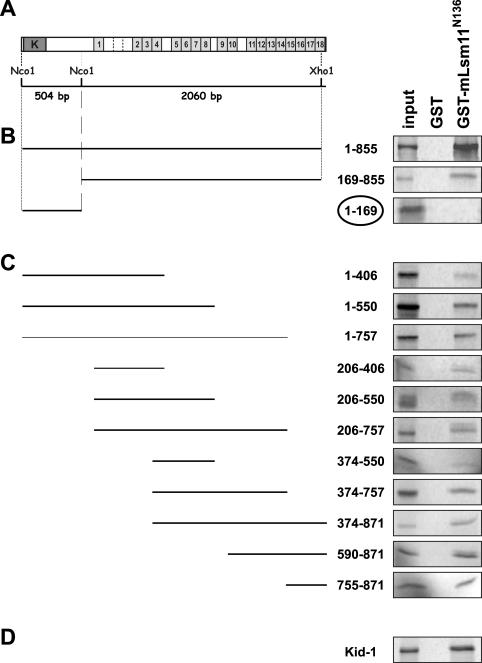
Figure 1.
The N-terminus of Lsm11 (GST-mLsm11N136) binds to the C2H2 zinc finger repeats of ZFP100. (A) Structure of ZFP100. Dark grey box labelled ‘K’, KRAB domain; light grey boxes, C2H2 zinc finger repeats; imperfect repeats are delineated by stippled lines. (B) GST pull-down assays with ZFP1–855, ZFP169–855 and ZFP1–169 encoded by subcloned NcoI and NcoI/XhoI restriction fragments as indicated in (A). (C) GST pull-down assays performed with ZFP100 truncations obtained by PCR (see Materials and Methods). The numbers indicate the ranges of amino acids of FL ZFP100 that are present in the various truncations. (D) GST pull-down assay performed with the C2H2 zinc finger protein Kid-1, a renal transcription factor from rat that is not related to histone RNA processing. All templates were linearized and subjected to coupled in vitro transcription/translation in the presence of [35S]methionine. The translation products were incubated with GST-mLsm11N136 or GST (negative control) immobilized on glutathione sepharose beads. The beads were washed, and the bound material was analysed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. Input, 1/10 the amount used in the binding assays was analysed directly. Note that only ZFP1–169 encoding the N-terminus of ZFP100 lacking zinc finger repeats but containing the KRAB domain does not bind to GST-mLsm11N136, whereas all fragments encoding zinc finger repeats bind efficiently.