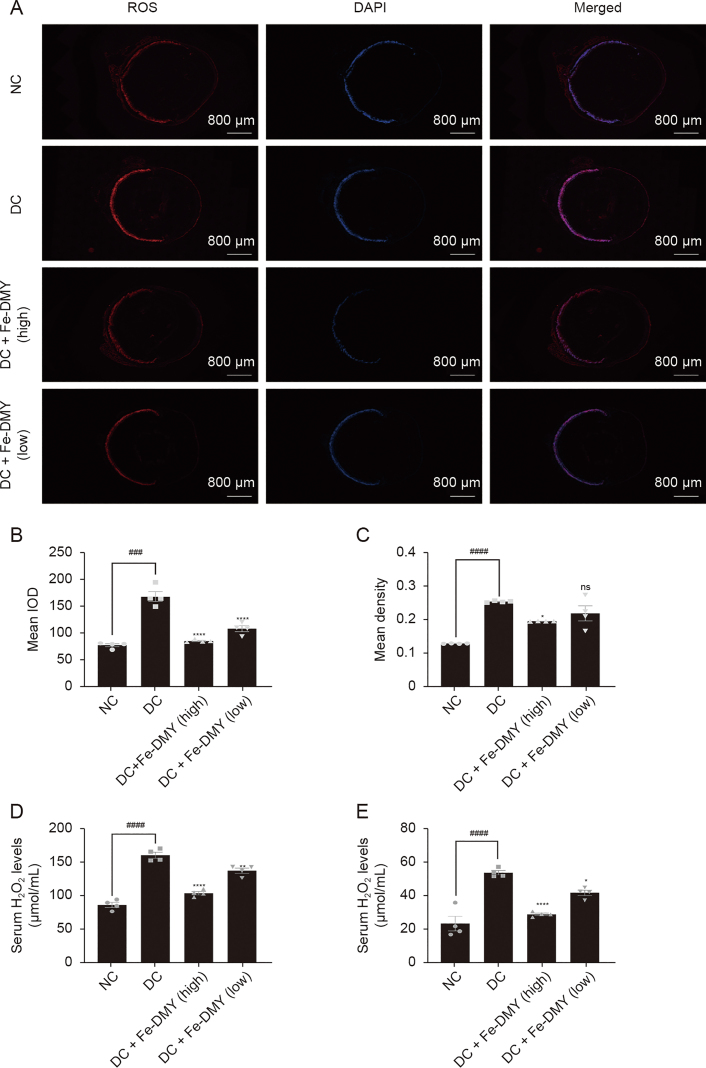
Fig. 8.
Fe-dihydromyricetin (DMY) nano-coordinated polymer particles (NCPs) reduce the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and H2O2 in diabetic retinopathy (DR) rats. (A) Immunofluorescence graph showing ROS levels in the retinas of different groups of rats. (B, C) Calculation of integral optical density (IOD) levels (B) and mean density (C) of ROS in the retinas of different groups of rats in Fig. 8A. (D, E) Levels of H2O2 in serum (D) and retinal tissue (E) in different groups. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), data represent mean ± standard error of mean (n = 4 per group). ∗ represented the significant difference between the administered (intervention) group and the DC group, and # represented the significant difference between the normal control (NC) group and the DC group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗/####P < 0.0001, compared with DC group; ns: not significant. DC + Fe-DMY (high): DC group treated with high-dose Fe-DMY NCPs (60 mg/kg). DC + Fe-DMY (low): DC group treated with low-dose Fe-DMY NCPs (10 mg/kg). DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.