Fig. 1.
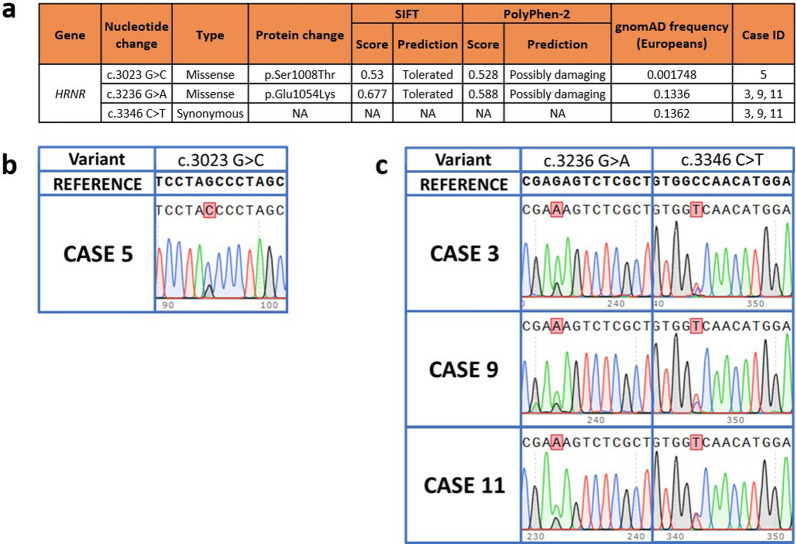
Characteristics of variants detected in HRNR in neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID). a Table showing in silico predictions of all variants detected across 12 NIID samples. Sorting Intolerant from Tolerant (SIFT) (https://sift.bii.a-star.edu.sg/) predicts if a substitution at the amino acid level affects protein function with scores ranging from 0 to 1. A variant is predicted damaging to protein function if the score is ≤ 0.05 and tolerated if the score is > 0.05. Polymorphism Phenotyping version 2 (PolyPhen-2) (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/) is a tool that predicts the possible effect of an amino acid substitution on protein function, with scores ranging from 0 (most probably benign) to 0.999 (most probably damaging). b The c.3023 G > C variant detected in Case 5, but not in any other cases, verifies the findings from Park and colleagues[1]. This variant of interest is highlighted in the chromatogram. c Missense variant c.3236 G > A and synonymous variant c.3346 c > T found in cases 3, 9 and 11. These variants of interest are highlighted in the chromatogram