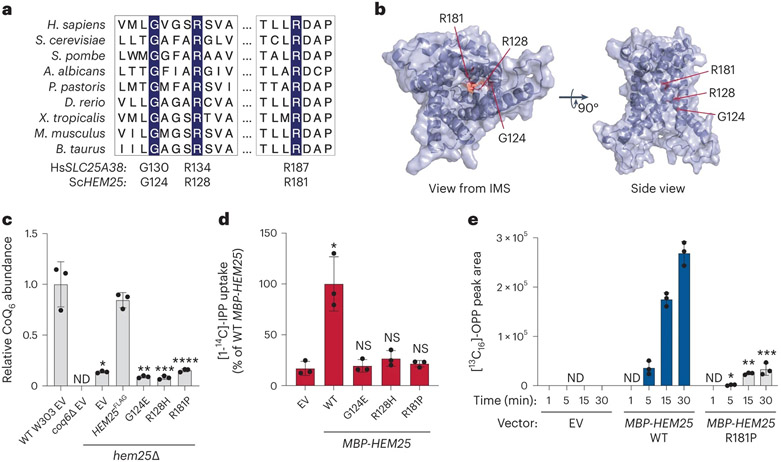
Fig. 5: Hem25p function is required for bacterial IPP import.
a, Multiple sequence alignment of HEM25 orthologues with residues mutated in congenital sideroblastic anaemia highlighted. b, Predicted structure of Hem25p showing the location of the disease-related residues. IMS, intermembrane space. c, Relative CoQ abundances in hem25Δ yeast carrying WT and mutant HEM25FLAGconstructs. Levels are relative to WT yeast carrying the empty expression vector (*P = 8.58 × 10−5, **P = 6.67 × 10−5, ***P = 6.78 × 10−5, ****P = 9.73 × 10−5 HEM25FLAG versus mutants or empty vector, mean ± s.d., n = 3 biologically independent samples, two-sided Student’s t-test). ND, not detected. d, Relative [1-14C]-IPP uptake by E. coli cells expressing WT or mutant MBP-Hem25p. Uptake levels reflect 30 min of incubation time and are relative to that of WT MBP-Hem25p (*P = 0.0063 empty vector versus WT HEM25, mean ± s.d., n = 3 biologically independent samples, two-sided Student’s t-test). NS, not significant. e, Normalized abundance of de novo synthesized [13C16]-OPP in E. coli cells expressing the empty vector (EV), WT MBP-Hem25p or the R181P MBP-Hem25p mutant (*P = 0.0116 WT versus R181P MBP-Hem25p at 5 min, **P = 4.1 × 10−5 WT versus R181P MBP-Hem25p at 15 min, ***P = 0.0001 WT versus R181P MBP-Hem25p at 30 min, mean ± s.d., n = 3 biologically independent samples, two-sided Student’s t-test). Numerical data are available as Source data.