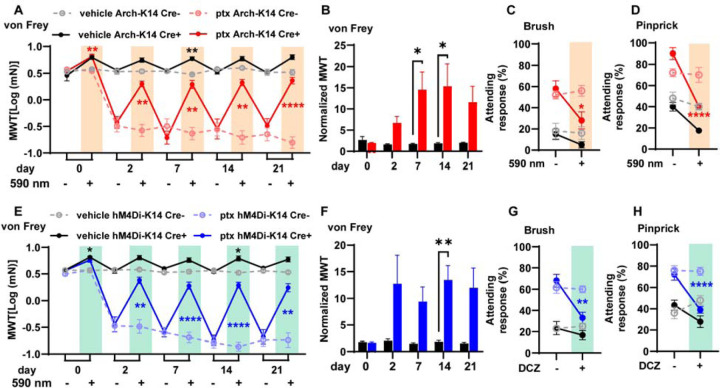
Fig. 1. Alleviation of paclitaxel-induced mechanical hypersensitivity through optogenetic and chemogenetic inhibition of keratinocytes:
(A) Comparison of mechanical withdrawal thresholds (MWT) for Arch-K14 Cre+ and Arch-K14 Cre- mice, pre- and post-paclitaxel or vehicle initiation; sample size: n = 7–10. (B) Fold change in withdrawal thresholds at each experimental day for vehicle treated Arch-K14 Cre+ and paclitaxel treated Arch-K14 Cre+ animals. Attending responses to dynamic brush (C) and noxious needle (D) hind paw stimuli, 10 days post-paclitaxel initiation, for both Arch-K14 Cre+ and Arch-K14 Cre- groups; n = 4–5. (E) Mechanical withdrawal thresholds (MWT) of both hM4Di-K14 Cre+ and hM4Di-K14 Cre- mice, assessed before (baseline) and following paclitaxel or vehicle administration; n = 9–12. (F) Fold change in withdrawal thresholds at each experimental day for vehicle treated hM4Di-K14 Cre+ and paclitaxel treated hM4Di-K14 Cre+ animals. (G) Attending responses to dynamic brush (on the left) and noxious needle (on the right) hindpaw stimulation, gauged 10 days post-paclitaxel administration, for hM4Di-K14 Cre+ and hM4Di-K14 Cre- cohorts; n = 9–12. Statistical analysis for (A, C, D, E, G, and H) was performed using a 3 way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons tests; for (B and F) using a 2 way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons tests *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P <0.0001. Error bars represent SE. For (A, C, D, E, G, and H) Black asterisks represent comparisons between vehicle treated animals while red or blue asterisks represent comparisons between paclitaxel treated animals. Schematic created with BioRender.com.