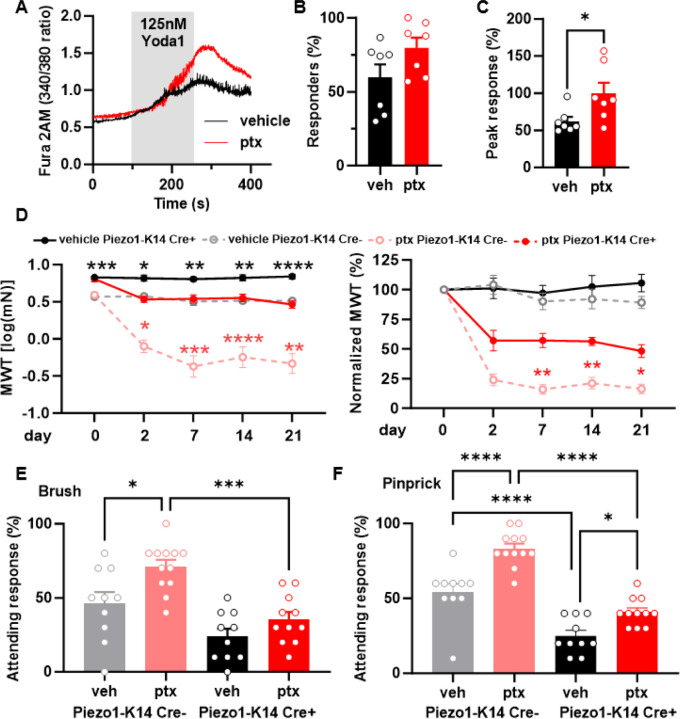
Fig. 4. Epidermal Piezo1 mediates paclitaxel-induced mechanical hypersensitivity.
(A) Representative traces showcasing calcium responses evoked by Yoda1 (125 nM) in keratinocytes derived from either vehicle or paclitaxel-treated mice. (B) The proportion of keratinocytes exhibiting a response to Yoda1. Dots depict the average count of responsive keratinocytes per mouse. (C) Magnitude of the calcium response to Yoda1. Dots depict the average peak calcium response observed in keratinocytes for each animal (n = 7, 60–100 cells per animal). (D) Comparison of mechanical withdrawal thresholds between Piezo1-K14 Cre+ and Piezo1-K14 Cre- mice, both before and after paclitaxel or vehicle treatment (left). Mechanical withdrawal threshold data normalized to baseline values (right); data sourced from 9–12 mice. Evaluation of responses to dynamic brush (E) and to the noxious needle (pinprick, F) hindpaw stimuli, at day 10 post-paclitaxel injection, in both Piezo1-K14 Cre+ and Piezo1-K14 Cre- groups; sample size: n = 9–12. Statistical analysis for (B and C) was performed using a Student’s T test; for (D) using a 3 way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; for (E and F) using a 2 way Anova with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P< 0.0001. Error bars represent SE. For figure (D), black asterisks represent comparisons between vehicle treated animals while red asterisks represent comparisons between paclitaxel treated animals. Schematic created with BioRender.com.