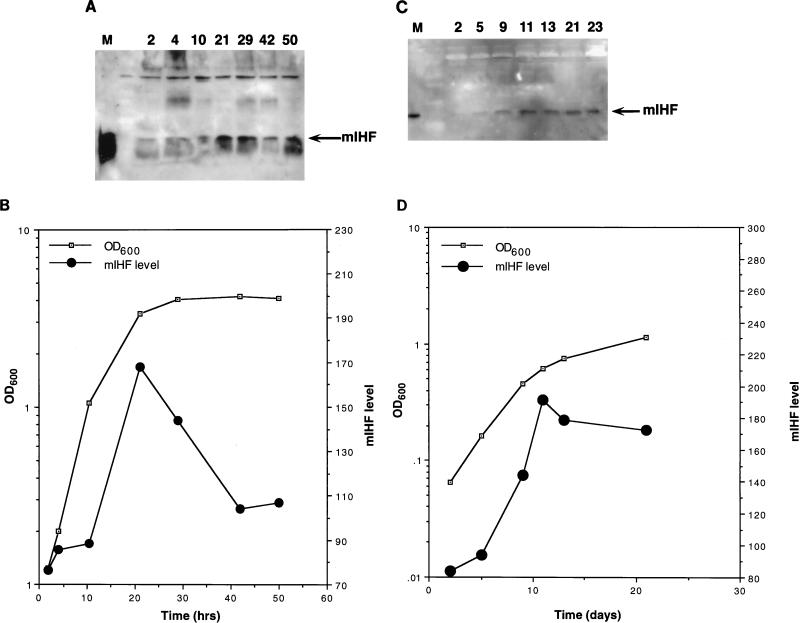
FIG. 2.
Growth phase dependency of mIHF. (A) Detection of M. smegmatis mIHF by immunoblotting. Following dilution of a saturated culture of M. smegmatis into fresh media, samples were removed at the times indicated (in hours), and cells were harvested by centrifugation. Samples were sonicated, normalized for total protein content, and electrophoresed on a sodium dodecyl sulfate–15% polyacrylamide gel. After transfer to polyvinylidine difluoride, the filter was probed with anti-mIHF serum and proteins were visualized by chemiluminescence. The marker lane (M) contains purified mIHF protein. (B) The optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of the bacterial culture used for panel A was determined at various times. The mIHF levels shown in panel A were quantitated by using NIH Image and are in arbitrary units. (C) Detection of BCG mIHF by immunoblotting. Samples of M. bovis BCG were removed at the indicated times (in days) after dilution of a saturated culture; cells were harvested, normalized for total protein content, and electrophoresed on a sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel. Following transfer to polyvinylidine difluoride, the filter was probed with anti-mIHF serum and detected by chemiluminescence. (D) The optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of the bacterial culture used for panel C was determined at various times. The mIHF levels shown in panel C were quantitated by using NIH Image and are in arbitrary units.