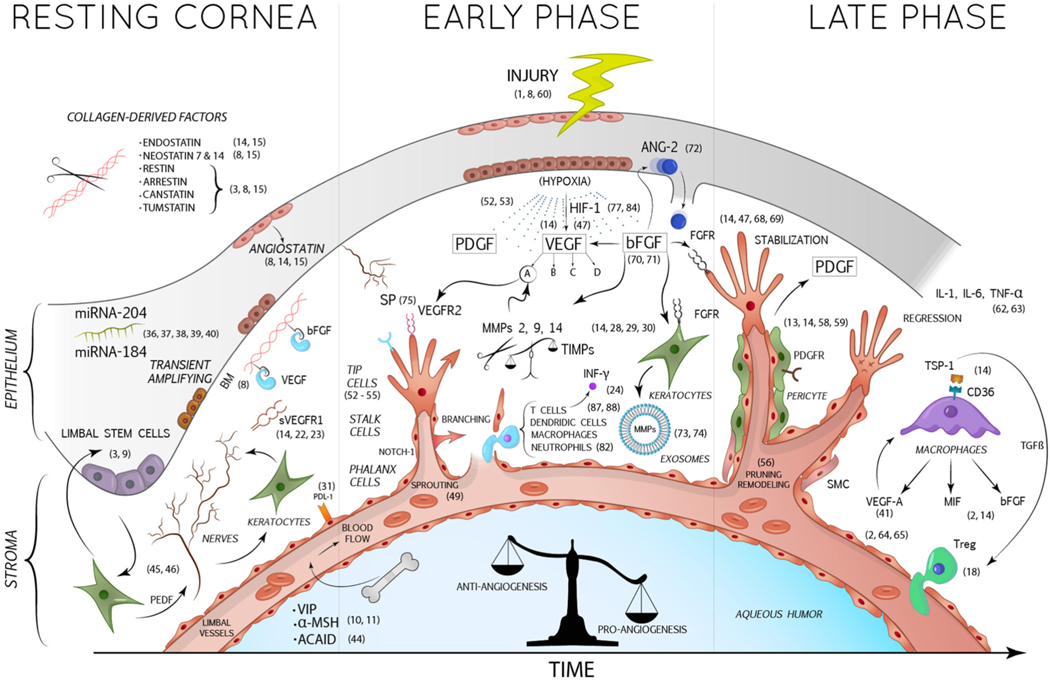
Fig. 1.
In the resting cornea, essential anti-angiogenic factors are expressed by corneal keratocytes and epithelial cells, such as sVEGFR1, a soluble trap for VEGF-A, and angiostatin. The cleavage of stromal collagen by proteases (as MMPs) allows the production of numerous collagen-derived anti-angiogenic factors. Furthermore, BM acts by sequestering and inactivating angiogenic factors such as VEGF and bFGF. The rich corneal innervation prevents the growth of new blood vessels, as explained in the article. Nerves in turn are stimulated by the PEDF produced by the keratocytes, assuming indirectly an anti-angiogenic role. The corneal epithelium is also responsible for the secretion of some miRNAs (as miRNA 184 and 204) with angio-static properties. Within the aqueous humor also circulate anti-angiogenic factors such as α-MSH and VIP. After corneal injuries, damaged corneal cells produce 3 important mediators: VEGF, bFGF and PDGF. VEGF-A binds its receptor VEGFR2 expressed on the endothelial cells of new infiltrating vessels, promoting their growth. bFGF induces the production of pro-angiogenic MMPs and exosomes by keratocytes and the release of ANG-2 by corneal epithelium. PDGF is relevant for the recruitment of pericytes and SMC, which stabilize newly formed vessels. In the final stages, macrophages contribute to the pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic environment by releasing VEGF-A, MIF and bFGF.
AbbreviationsBM: Bowman’s membrane; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; FGFR: Fibroblast growth factor receptor; PEDF: Pigment epithelium-derived growth factor; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; sVEGFR-1: Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; TIMPs: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases; INF-γ: Interferon γ; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; TSP: Trombospondin; MIF: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor; ANG-2: Angiopoietin-2; SP: Substance P; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1; miRNA: Micro RNA; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide; α-MSH: α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone; ACAID: Anterior chamber-associated immune deviation; SMC: Smooth muscle cells.