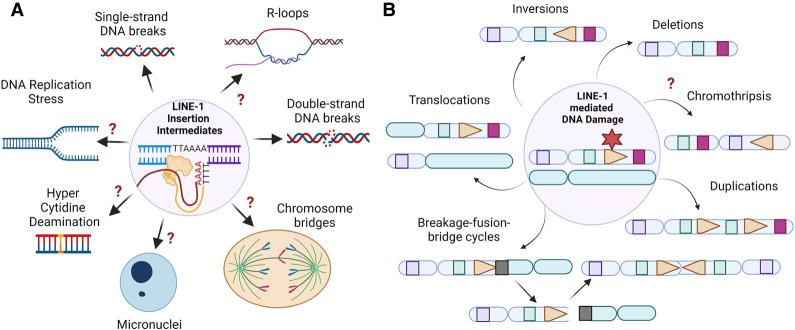
Figure 5.
LINE-1 retrotransposition is a source of DNA damage and genome instability. (A) LINE-1 retrotransposition causes DNA damage in cells. Shown is a diagram highlighting the multiple types of DNA damage that might be induced by LINE-1 retrotransposition, including chromosomal breaks, single-strand DNA breaks, DNA replication stress, DNA–RNA hybrids, abnormal nuclear structures such as chromosome bridges and micronuclei, and indirect activation of aberrant cytidine deamination by APOBEC proteins. (B) LINE-1-mediated DNA damage can be a source of chromosomal structural variants (SVs): deletions, duplications, translocations, inversions, breakage–fusion–bridge cycles, and chromothripsis.