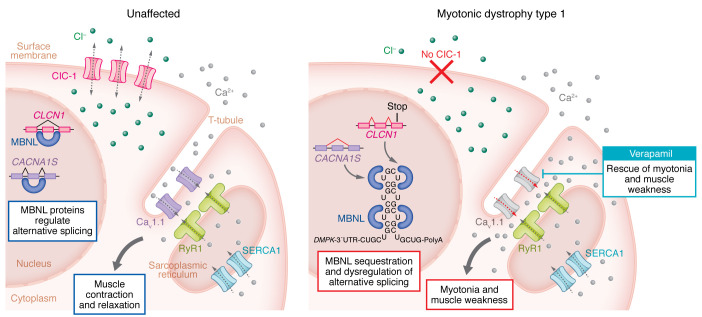
Figure 1. The combined effects of ion channels from mis-spliced RNA cause myotonia and muscle weakness in DM1.
In unaffected muscle tissues, MBNL correctly regulates splicing of the alternative exons in CLCN1 and CACNA1S. This process results in expression of the adult isoforms of the chloride and calcium channels, which, together with SERCA1 and RyR1, facilitate proper muscle contraction and relaxation. In DM1, MBNL sequestration on expanded CUG repeats causes the dysregulation of CLCN1 and CACNA1S alternative splicing. The inclusion of a CLCN1 fetal exon leads to a frameshift and premature stop codon, causing ClC-1 loss. Mis-splicing also leads to expression of the Cav1.1 fetal isoform, which has an increased calcium current compared with the adult isoform. The combined loss of ClC-1 and expression of the fetal Cav1.1 isoform leads to severe myopathy that can be rescued pharmacologically by blocking the calcium channel using verapamil.