Figure 4:
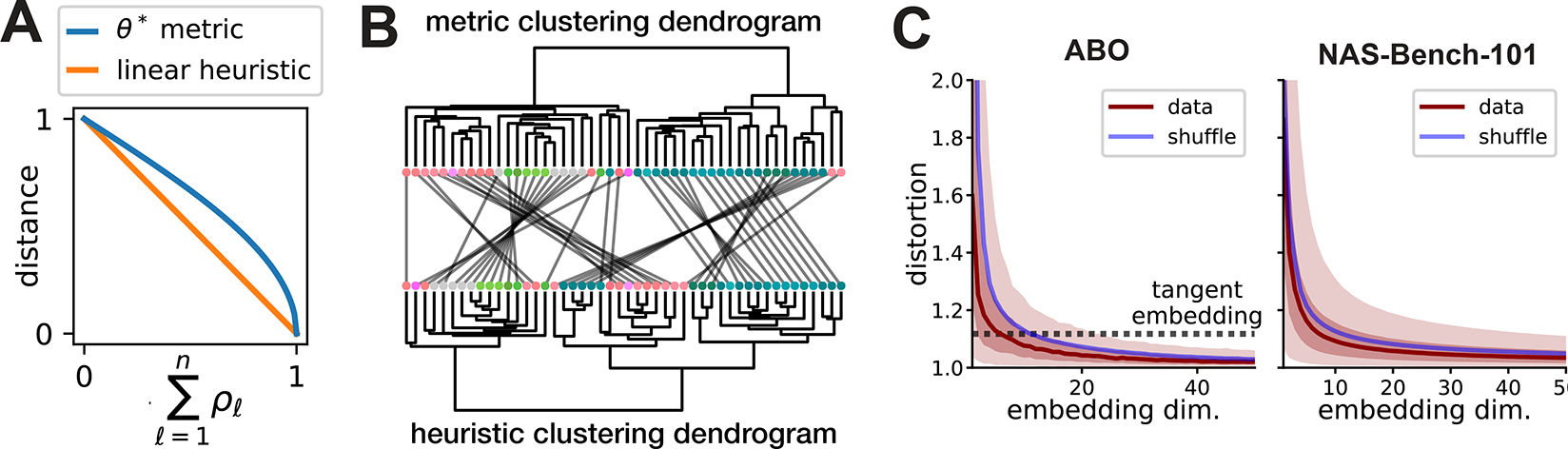
(A) Comparison of metric and linear heuristic. (B) Metric and linear heuristic produce discordant hierarchical clusterings of brain areas in the ABO dataset. Leaves represent brain areas that are clustered by representational similarity (see Fig. 1C), colored by Allen reference atlas, and ordered to maximize dendrogram similarities of adjacent leaves. In the middle, grey lines connect leaves corresponding to the same brain region across the two dendrograms. (C) ABO and NAS-Bench-101 datasets can be accurately embedded into Euclidean spaces. Dark red line shows median distortion. Light red shaded region corresponds to 5th to 95th percentiles of distortion, dark red shaded corresponds to interquartile range. The mean distortion of a null distribution over representations (blue line) was generated by shuffling the inputs independently in each network.
