Figure 3.
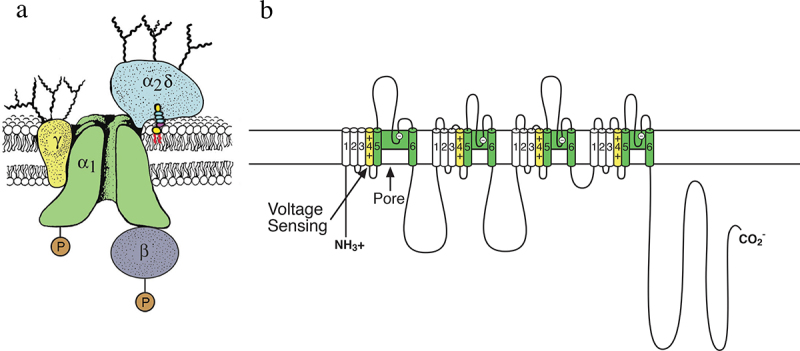
The subunit structure of calcium channels purified from skeletal muscle. a) a biochemical model of the skeletal muscle calcium channel taken from the original description of the subunit structure of skeletal muscle Ca2+ channels but with the mature α2δ subunit depicted following proteolytic processing, disulfide bond formation and attachment of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Adapted from Takahashi et al., 1987 [48]. P, sites of phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Ψ, sites of N-linked glycosylation. b) transmembrane folding models of the CaV1.1 subunits. Predicted alpha helices are depicted as cylinders. The lengths of lines correspond approximately to the lengths of the polypeptide segments represented. Adapted from Catterall, 1991 [49].
