Figure 5.
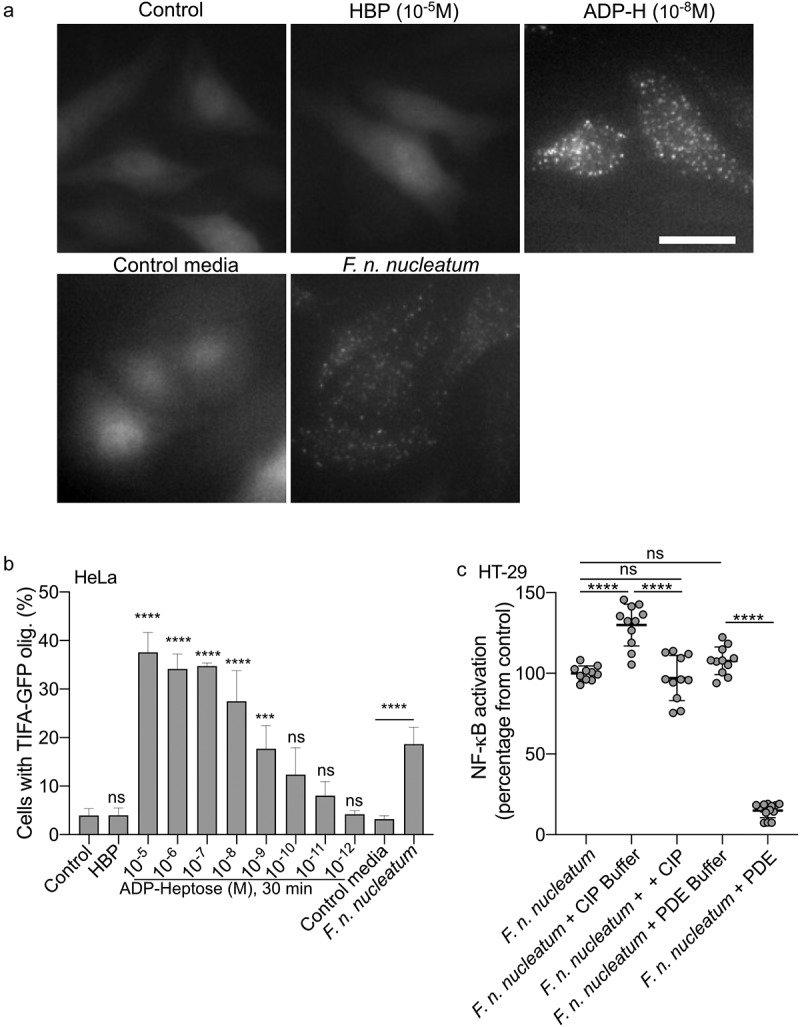
F. nucleatum NF-κB activating molecule has the biological features of the ALPK1 ligand ADP-heptose. (a,b) cells were treated with digitonin and non-inoculated control medium, F. nucleatum supernatants, HBP (10−5M) or ADP-H (10−8M). in A: Representative pictures of cells with TIFAsomes at 30 min in TIFA-GFP-expressing HeLa cells (scale bar: 20 μm). In B, quantification of TIFAsomes in each condition as in a from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (c) F. nucleatum supernatant was untreated, treated with calf intestine alkaline phosphatase (CIP), with C. adamanteus phosphodiesterase (PDE) or their respective buffer (CIP buffer and PDE buffer) prior to stimulation of HT-29-NF-κB reporter cells for 24 h. NF-κB activation was measured by SEAP secretion and results were expressed as mean change (%) ± SD toward F. nucleatum supernatant-stimulated cells. Data represent ≥ 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (for B, the samples were compared to their respective control: control for ADP-H and HBP and control media for F. nucleatum supernatants). ****P < ,0001; ***P < ,001; **P < ,01; *P < ,05; P < 0.05 was considered as not significant (ns).
