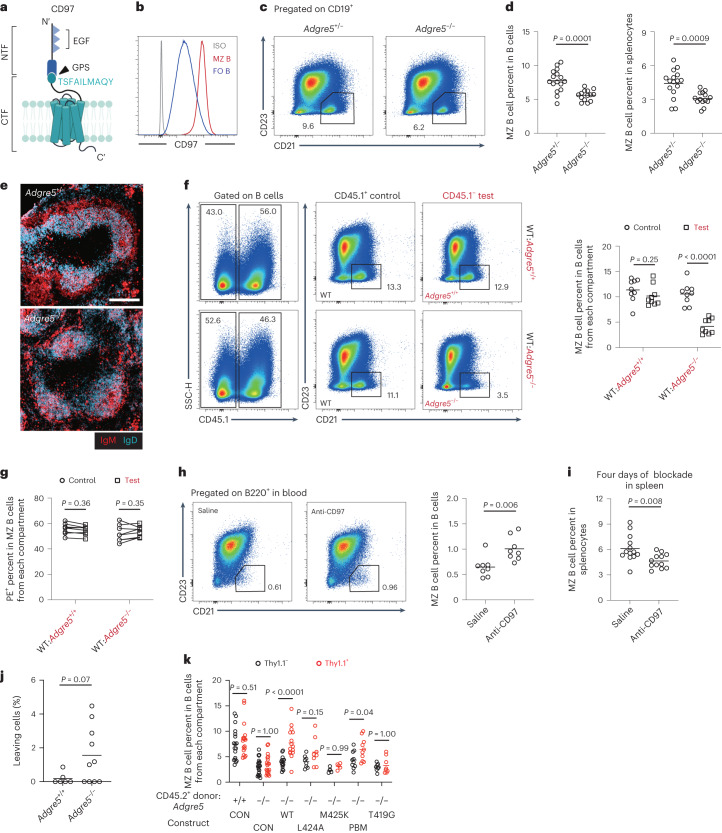
Fig. 2. CD97 is required for MZ B cell homeostasis.
a, Structural components of CD97. Triangles indicate EGF domains. The ten amino acids (419–428) following the GPS are indicated. b, Representative histogram plot of CD97 on MZ and follicular (FO) B cells; ISO, isotype control. c,d, Flow cytometry profiles (c) and frequencies of MZ B cells in B cells (d; left) and total splenocytes (d; right) in Adgre5−/− (n = 16) and control (n = 14) mice. e, Distribution of IgMhi MZ (red) and IgDhi follicular (blue) B cells in indicated spleens; scale bar, 200 μm. Sections are representative of multiple cross-sections from at least three mice of each type. f, Flow cytometry profiles (left) and frequencies (right) of MZ B cells of the indicated genotypes in WT:Adgre5−/− (n = 9) and control (n = 9) chimeras. g, Frequencies of in vivo anti-CD45-phycoerythrin (PE)-labeled MZ B cells of the indicated genotypes in WT:Adgre5−/− (n = 8) and control (n = 8) chimeras. Lines connect data from the same animals. h, Flow cytometry profiles (left) and frequencies (right) of MZ B cells in blood in WT mice 3 h after treatment with anti-CD97 (n = 8) or saline (n = 8). i, Frequencies of MZ B cells in the spleen in WT mice after 4 d of treatment with anti-CD97 (n = 13) or saline (n = 12). j, Frequencies of ‘leaving cells’ (GFP+ B cells that enter large vessels) in mice reconstituted as in Fig. 1a with Adgre5−/− (n = 10) and Adgre5+/+ (n = 6) MZ B cells. See corresponding Supplementary Videos 5 and 6. k, BM chimeras were reconstituted with 10% non-transduced CD45.1 WT and 90% CD45.2 Adgre5+/+ or Adgre5−/− BM transduced with retroviral constructs encoding Adgre5 WT (n = 15) or its mutants (n = 8 in L424A, n = 5 in M425K, n = 10 in PBM and n = 8 in T419G) or empty vector (CON; n = 18 in Adgre5+/+ and n = 20 in Adgre5−/−). The graph shows the frequencies of MZ B cells in Thy1.1+ or Thy1.1− B cells. Data are pooled from four (d and i), two (f–h), five (j) or six (k) independent experiments. Each symbol represents one mouse, and lines denote means. Statistical significance was tested by two-tailed t-test (d, h, i and j) or two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Sidak’s multiple-comparisons test (f, g and k).