Table 2.
Multivariable Cox regression for mortality by total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C, and TG.
| No. of patients | Events | Person-years | Incidence rate (per 10,000 py) | Age and sex adjusted hazard ratio (95%CI) | Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio (95%CI) | HR (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Association between TC at cancer diagnosis and the risk of all-cause death by centile groups | |||||||
| 1st–5th (≤ 97 mg/dL) | 3012 | 1143 | 15,924 | 717.8 | 1.79 (1.66–1.93) |  |
1.54 (1.43–1.66) |
| 6th–20th (97–128 mg/dL) | 9217 | 2711 | 52,843 | 513.0 | 1.46 (1.38–1.55) | 1.26 (1.19–1.34) | |
| 21st–40th (129–151 mg/dL) | 12,006 | 2756 | 72,626 | 379.5 | 1.20 (1.13–1.27) | 1.09 (1.03–1.16) | |
| 41st–60th (152–171 mg/dL) | 11,467 | 2222 | 70,407 | 315.6 | 1.09 (1.03–1.16) | 1.03 (0.97–1.09) | |
| 61st–80th (172–196 mg/dL) | 11,903 | 1310 | 54,828 | 238.9 | Reference | Reference | |
| 81st–95th (197–233 mg/dL) | 8690 | 1970 | 74,323 | 265.1 | 0.96 (0.89–1.03) | 1.02 (0.95–1.09) | |
| 96th–100th (> 233 mg/dL) | 2922 | 512 | 18,428 | 277.8 | 1.20 (1.09–1.33) | 1.28 (1.16–1.41) | |
| Association between LDL-C at cancer diagnosis and the risk of all-cause death by centile groups | |||||||
| 1st–5th (≤ 57 mg/dL) | 646 | 197 | 2,579 | 76.4 | 2.10 (1.74–2.54) | 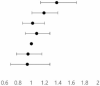 |
1.38 (1.14–1.68) |
| 6th–20th (57–79 mg/dL) | 1811 | 365 | 8,374 | 43.6 | 1.56 (1.33–1.83) | 1.19 (1.01–1.40) | |
| 21st–40th (79–97 mg/dL) | 2427 | 344 | 12,306 | 28.0 | 1.17 (1.00–1.38) | 1.02 (0.87–1.20) | |
| 41st–60th (97–115 mg/dL) | 2548 | 296 | 13,110 | 22.6 | 1.09 (0.92–1.28) | 1.08 (0.91–1.28) | |
| 61st–80th (115–136 mg/dL) | 2368 | 252 | 12,546 | 20.1 | Reference | Reference | |
| 81st–95th (136–167 mg/dL) | 1786 | 160 | 9,560 | 16.7 | 0.89 (0.73–1.08) | 0.95 (0.78–1.16) | |
| 96th–100th (> 167 mg/dL) | 598 | 48 | 3,142 | 15.3 | 0.89 (0.65–1.22) | 0.94 (0.69–1.28) | |
| Association between HDL-C at cancer diagnosis and the risk of all-cause death by quartile groups | |||||||
| Q1 (≤ 40 mg/dL) | 3270 | 772 | 14,593 | 529 | 2.65 (2.24–3.14) | 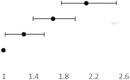 |
2.10 (1.77–2.50) |
| Q2 (40–50 mg/dL) | 3097 | 445 | 15,895 | 280 | 1.72 (1.44–2.05) | 1.66 (1.39–1.98) | |
| Q3 (50–61 mg/dL) | 2798 | 266 | 15,087 | 176.3 | 1.24 (1.03–1.50) | 1.27 (1.05–1.54) | |
| Q4 (> 61 mg/dL) | 3022 | 179 | 16,054 | 111.5 | Reference | Reference | |
| Association between TG at cancer diagnosis and the risk of all-cause death by quartile groups | |||||||
| Q1 (≤ 73 mg/dL) | 3499 | 487 | 18,784 | 259.3 | 1.02 (0.90–1.15) |  |
0.96 (0.84–1.09) |
| Q2 (73–99 mg/dL) | 3413 | 520 | 16,961 | 306.6 | 1.02 (0.90–1.15) | 0.95 (0.83–1.07) | |
| Q3 (99–138 mg/dL) | 3440 | 524 | 17,286 | 303.1 | 1.00 (0.88–1.13) | 0.93 (0.82–1.06) | |
| Q4 (> 138 mg/dL) | 3381 | 500 | 17,871 | 279.8 | Reference | Reference | |
Multivariable-adjusted model was adjusted for age, sex, BMI, use of lipid-lowering agents, presence of CKD, DM, and HTN, smoking status, alcohol consumption, and cancer type.
CKD chronic kidney disease, DM diabetes mellitus, HDL-C high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HR hazard ratio, HTN hypertension, LDL-C low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG triglyceride, TC total cholesterol, CI confidence interval.
