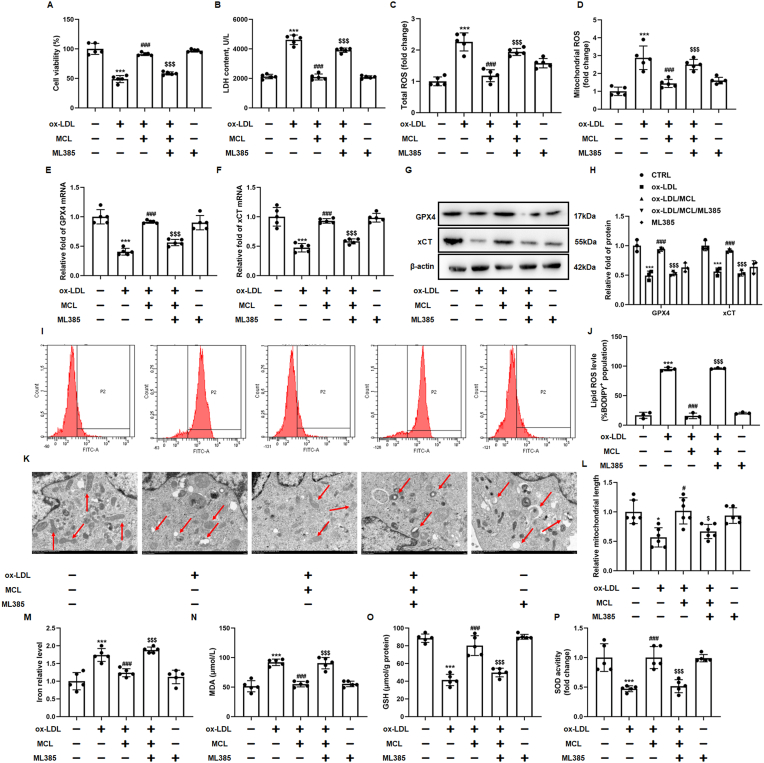
Fig. 6.
ML385 abolishes the anti-ferroptosis and antioxidant effect of MCL. 5 μM ML385 was pretreated in 1 h, then 10 μM MCL is added into the medium, after 1 h, 100 μg/ml ox-LDL is also added into the medium for 48 h. Immunofluorescence is used to observed the ROS staining, microplate reader is used to evaluated the intensity of ROS. The macrophages are divided into five groups, control groups, ox-LDL groups (ox-LDL, 100 μg/ml), MCL group (pretreated with 10 μM MCL for 1h, then combined with 100 μg/ml ox-LDL for 24 h), ML385 group (pretreated with 5 μM ML385 and 10 μM for 1 h, then combined with 100 μg/ml ox-LDL for 48 h), ML385 alone group (5 μM ML385). (A). CCK-8 assay was used to analysis cell viability. N = 5; (B). LDH level in supernatant. N = 5; (C, D) Total and mitochondrial ROS level. N = 5; (E, F) Total artery RNA was extracted from the cells, and mRNA levels of GPX4 and xCT were detected; N = 5. (G, H) Total cell lysates were extracted, and protein levels of GPX4 and xCT were detected; N = 3. (I, J). The lipid ROS level was evaluated by flow cytometry using C11-Bodipy fluorescent probe. N = 3; (K, L). Representative transmission electron microscopy pictures of macrophages and the quantification of relative mitochondrial length. N = 6; (M–P). The levels of MDA, GSH, SOD activity and iron content were measured in macrophages by commercial kits. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs control group. #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 vs ox-LDL group. $p < 0.05, $$$p < 0.001 vs MCL + ox-LDL group.