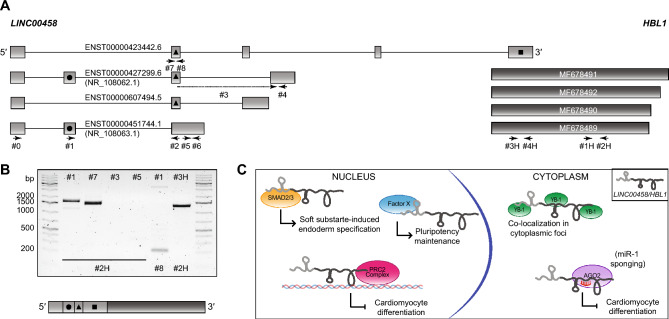
Figure 4.
Relationship of the HBL1 gene with the LINC00458 gene. (A) Selected LINC00458 isoforms according to GENCODE V39 12/2022 (light gray) and HBL1 mRNAs from GenBank (dark gray). GENCODE transcript numbers and NCBI RefSeq numbers are indicated. The localization of primers is depicted by arrows and single digit numbers for LINC00458 and H followed by single digit numbers for HBL1. Exons are represented as boxes, and introns are represented as lines. (B) RT-PCR products amplified with indicated primers selected such as to detect the presence of amplicons that encompass both LINC00458 and HBL1 sequences were separated by electrophoresis (upper panel). Forward primers are indicated at the top of the gel and reverse primers at the bottom. See Fig. 4A for the localization of the primers within the transcripts. PCR products amplified using primer #1 (as well as #0) combined with #2H were purified from the gel and subjected to Sanger sequencing, and the resulting sequence corresponded to the indicated LINC00458 exons and HBL1 (lower panel). (bp = base pairs). The original raw agarose gel image is presented in Supplementary Fig. S8A. (C) Model of LINC00458/HBL1 cellular function proposed based on published data and our work. We propose that LINC00458/HBL1 interacts with its binding partners and fulfils its diverse nuclear and cytoplasmic functions through separate functional domains encompassed within its sequence. The sequence corresponding to the 5′ exons of LINC00458 is shown in light gray, and the 3′ end containing the HBL1 sequence is shown in dark gray.