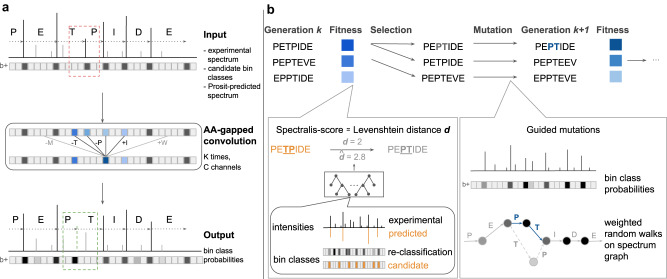
Fig. 1. Bin reclassification and overview of Spectralis.
a The deep learning architecture for bin reclassification consisting of AA-gapped convolutions for correcting erroneous bin classes (red box) of an input candidate peptide. Input for the model are the binned experimental intensities, the initial bin class labels for y-ions and b-ions, and the binned Prosit-predicted intensities for the input peptide sequence. The model outputs the probabilities for each bin to contain a peak labeled as a y-ion and as a b-ion. b Spectralis-EA is an evolutionary algorithm. Peptide sequences from a generation k are selected based on their fitness to define the next generation k + 1. The fitness, or Spectralis-score, is an estimate of the Levenshtein distance from the input peptide (orange) to the correct peptide (gray). It is obtained with a random forest taking features computed from the experimental and Prosit-predicted spectra and from the output of the bin reclassification model (left inset) as input. The peptides selected for the next generation are mutated by performing random walks along the spectrum graph favoring nodes stemming from bins with high probabilities (right inset).