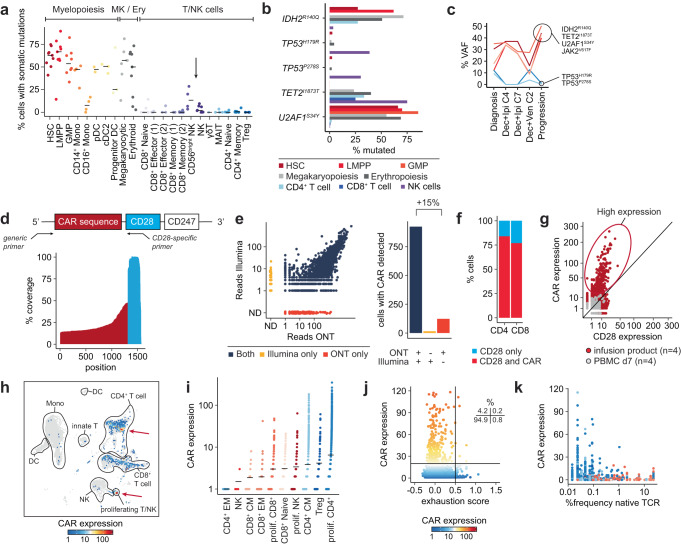
Fig. 7. Tracking of somatic mutations and CAR transcripts in T and NK cells.
a Percentage of cells with detected somatic nuclear mutations across 22 hematopoietic cell types in 9 AML cases for a total of 17,911 cells. Arrow indicates NK cells. MK - megakaryopoiesis, Ery erythropoiesis, T/NK T and NK cells. b Percentage of cells with detected somatic nuclear mutations across hematopoietic cell compartments in AML1002. TP53R179H and TP53P278S are enriched in NK cells (purple). c Longitudinal clinical amplicon sequencing of bulk bone marrow-derived DNA demonstrates separation of NK-associated mutations (TP53R179H and TP53P278S) from AML-associated mutations in AML1002 (IDH2R140Q, TET2I1873T, U2AF1S34Y, and JAK2V617F). d PCR scheme demonstrating the amplification strategy of CAR transcripts with a CD28-specific primer. The coverage plot demonstrates the amplification of wildtype CD28 (blue) and fusion transcripts spanning into the CAR domain (red). e Read distribution with nanoranger on the Oxford Nanopore platform (ONT) compared to short-read sequencing (Illumina) as number of reads per cell barcode (left). The bar plot (right) shows the number of cells in which a CAR transcript was detected with both technologies (+/+), only with Illumina (-/+) or only with ONT (+/-). ND not detected. f Quantification of cells that only have wildtype CD28 transcripts (blue, CD28 only) versus cells with at least one CAR transcript (red, CAR, and CD28) in one CAR T cell infusion product. g, h Identification of CAR T cells with high expression of CAR transcripts by comparison with wildtype CD28 expression levels (g). Projection of CAR T cell detection on UMAP annotated by predicted cell types based on the PBMC reference dataset provided by Seurat (h). Data shown for four infusion products and four PBMC samples at day 7 after CAR T cell infusion. Red arrows indicate cells with high CAR expression. i Expression levels of CAR transcripts across ten predicted cell types in a total of 6504 cells. Expression levels of CAR transcripts compared to exhaustion score (calculated from expression of PDCD1, CTLA4, TIGIT, HAVCR2, TOX, LAG3, and ENTPD1) (j) and percentage clonal expansion of the native T cell receptor (TCR) relative to all detected TCRs within the library (k).