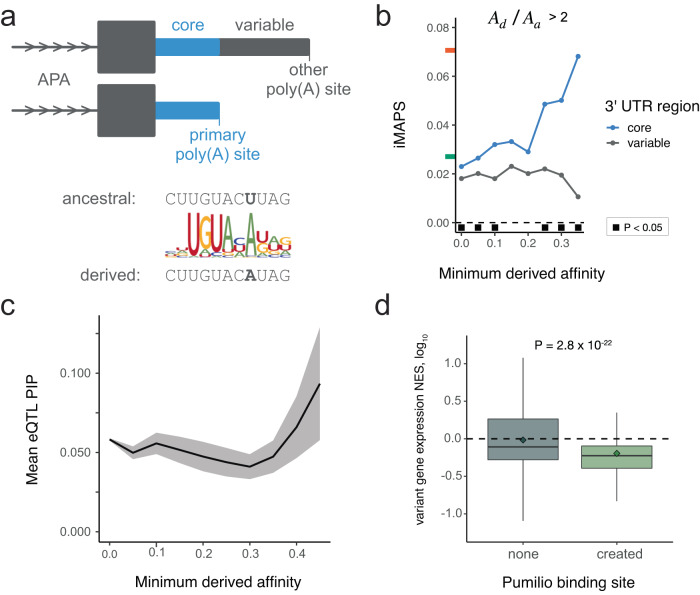
Fig. 3. The impact of de novo Pumilio binding sites created by genetic variants.
a Top: Illustration of the “core” 3ʹ UTR region (blue) upstream of the primary (most utilized) poly(A) site and the “variable” 3ʹ UTR region (gray) present only in isoforms resulting from use of secondary poly(A) sites. Bottom: Schematic illustrating an example of Pumilio binding site creation. b Variants creating Pumilio binding sites in core 3ʹ UTR regions are under strong negative selection. Ad = derived affinity, Aa = ancestral affinity. Black squares indicate one-sided Fisher Exact Tests with P < 0.05. Exact P values and the number of variants analyzed are included in Supplementary Data 1. c eQTL variants that create high-affinity Pumilio sites typically have higher PIP values. Shaded area indicates mean +/- standard error. d eQTL variants creating Pumilio sites (n = 448 eQTLs) are also associated with decreased transcript levels relative to those with no site (n = 70,318 eQTLs), consistent with the destabilizing impact of Pumilio binding. The P value shown is the result of a one-sided Wilcoxon Rank Sum test. NES = log10 normalized effect size. Diamonds indicate mean NES values. Lines within boxes indicate median NES values. Boxes extend from first quartile to third quartile values. Whiskers extend to 1.5x the interquartile range.