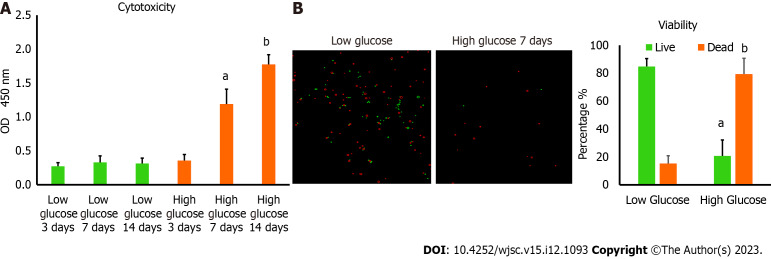
Figure 1.
Culturing human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in high glucose reduced their viability. A: Lactate dehydrogenase cytotoxicity assay revealed higher level of cytotoxicity in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAD-MSCs) cultured in high glucose for 7 and 14 d compared to cells cultured in low glucose. n = 5, aP < 0.01 compared to low glucose 7 d, bP < 0.01 compared to low glucose 14 d; B: The percentage of cells viability detected by 0.4% Trypan blue showed significant reduction in the number of viable hAD-MSCs after being cultured in high glucose for 7 d. Fluorescent images of live and dead cells were obtained using Corning® CytoSmart Cell Counter. n = 5. n = 5, aP < 0.01 compared to live cells in low glucose 7 d, bP < 0.01 compared to dead cells in low glucose 7 d.